Use of rMPB70 protein and ESAT-6 peptide as antigens for comparison of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent, immunochromatographic, and latex bead agglutination assays for serodiagnosis of bovine tuberculosis
- PMID: 16145098
- PMCID: PMC1234133
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.9.4498-4506.2005
Use of rMPB70 protein and ESAT-6 peptide as antigens for comparison of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent, immunochromatographic, and latex bead agglutination assays for serodiagnosis of bovine tuberculosis
Abstract
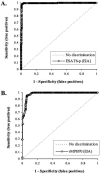
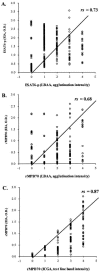
Current assays used to detect Mycobacterium bovis infection lack accuracy, especially for recently infected animals, or are impractical for rapid field diagnostic applications. To overcome these limitations with serological assays, a synthetic peptide derived from early secretory antigenic target 6 (ESAT6-p) and a recombinant major secreted immunogenic protein (rMPB70) of M. bovis were used in an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (EIA), an immunochromatographic assay (ICGA), and a latex bead agglutination assay (LBAA). Sera from noninfected, M. bovis-infected, or M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis-infected (by natural and experimental routes) animals were evaluated. Receiver operating characteristic analysis comparing optical density values from the EIA with results of bacterial culture or skin test, the reference test, established suitable cutoff values for assessing sensitivity and specificity. The EIA and LBAA, respectively, had sensitivities of 98.6 and 94.8%, specificities of 98.5 and 92.6%, and kappa values of 0.97 and 0.88 with ESAT6-p. The EIA, ICGA, and LBAA, respectively, had sensitivities of 96.8, 83.0, and 86.7%, specificities of 90.1, 99.4, and 97.8%, and kappa values of 0.87, 0.85, and 0.83 with rMPB70. Examination of serial samples of sera collected from experimentally M. bovis-infected cattle and deer revealed that ESAT6-p-specific responses developed early after infection whereas responses to rMPB70 developed later in the course of disease. The advantage of the LBAA and ICGA as initial tests for multiple species is a rapid reaction obtained in 2 to 3 h by LBAA or 20 min by ICGA without species-specific secondary antibodies under field conditions, thus allowing immediate segregation of suspect animals for further testing before culling.
Figures

References
-
- Altman, D. G. 1991. Practical statistics for medical research, p. 403-409. Chapman & Hall, Ltd., London, United Kingdom.
-
- Amadori, M., K. P. Lyashchenko, M. L. Gennaro, J. M. Pollock, and I. Zerbini. 2002. Use of recombinant proteins in antibody tests for bovine tuberculosis. Vet. Microbiol. 85:379-389. - PubMed
-
- Beck, J. R., and E. K. Schultz. 1986. The use of relative operating characteristic (ROC) curves in test performance evaluation. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 110:13-20. - PubMed
-
- Billman-Jacobe, H., A. J. Radford, J. S. Rothel, and P. R. Wood. 1990. Mapping of the T and B cell epitopes of the Mycobacterium bovis protein MPB70. Immunol. Cell Biol. 68:359-365. - PubMed
-
- Buddle, B. M., T. J. Ryan, J. M. Pollock, P. Andersen, and G. W. de Lisle. 2000. Use of ESAT-6 in the interferon-gamma test for diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis following skin testing. Vet. Microbiol. 80:37-46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

