Reproducibility of low galactomannan enzyme immunoassay index values tested in multiple laboratories
- PMID: 16145143
- PMCID: PMC1234072
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.9.4796-4800.2005
Reproducibility of low galactomannan enzyme immunoassay index values tested in multiple laboratories
Abstract
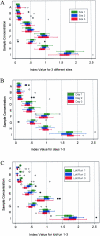
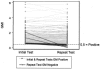
The Platelia galactomannan enzyme immunoassay is a commercially available nonculture method for diagnosing invasive aspergillosis. Recently, steps have been taken to improve sensitivity; specifically, a low (0.5 to 0.7) galactomannan index (GMI) value to determine positivity has been validated by multiple groups. We evaluated the intra-assay and interassay reproducibility at low index levels using three different kit lots on three different days in three different microbiology laboratories. Clinical and spiked sera were blinded and sent with galactomannan enzyme immunoassay (EIA) kits to the participating laboratories. We also prospectively collected data on all galactomannan EIAs performed between 1 September 2003 and 21 July 2004 at the University of Washington Medical Center microbiology laboratory to assess reproducibility of clinical samples analyzed in "real time." From the multilaboratory study, a total of 836 results were available for evaluation. Reproducibility was excellent between laboratories and on different days. Significant variability was seen between runs/lots, which may in part be associated with different threshold control values in different kits. Among the 1,410 clinical samples that were prospectively analyzed, 168 (90%) were confirmed to be positive on repeat testing (GMI, > or =0.5). Among the 19 (10.2%) initially positive samples not confirmed on repeat testing, the majority had a GMI at the threshold of the assay (between 0.5 and 0.7). Our findings suggest that the Platelia galactomannan immunoassay has good reproducibility. However, changes in GMI levels when different kit lots are used, and single samples with low-positive (GMI of 0.5 to 0.7) indices, should be interpreted with caution.
Figures
References
-
- Ascioglu, S., J. H. Rex, B. De Pauw, J. E. Bennett, J. Bille, F. Crokaert, D. W. Denning, J. P. Donnelly, J. E. Edwards, Z. Erjavec, D. Fiere, O. Lortholary, J. Maertens, J. F. Meis, T. F. Patterson, J. Ritter, D. Selleslag, P. M. Shah, D. A. Stevens, and T. Walsh. 2002. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 34:7-14. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland, W. S. 1993. Visualizing data. Hobart Press, Summit, N.J.
-
- Herbrecht, R., V. Letscher-Bru, C. Oprea, B. Lioure, J. Waller, F. Campos, O. Villard, K.-L. Liu, S. Natarajan-Ame, P. Lutz, P. Dufour, J.-P. Bergerat, and E. Candolfi. 2002. Aspergillus galactomannan detection in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 20:1898-1906. - PubMed
-
- Lin, S.-J., J. Schranz, and S. M. Teutsch. 2001. Aspergillosis case-fatality rate: systematic review of the literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 32:358-366. - PubMed
-
- Machetti, M., M. Feasi, N. Mordini, M. T. Van Lint, A. Bacigalupo, J. P. Latge, J. Sarfati, and C. Viscoli. 1998. Comparison of an enzyme immunoassay and a latex agglutination system for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in bone marrow transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 21:917-921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

