A comparative study of a theoretical neural net model with MEG data from epileptic patients and normal individuals
- PMID: 16146568
- PMCID: PMC1236964
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4682-2-37
A comparative study of a theoretical neural net model with MEG data from epileptic patients and normal individuals
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to compare a theoretical neural net model with MEG data from epileptic patients and normal individuals.
Methods: Our experimental study population included 10 epilepsy sufferers and 10 healthy subjects. The recordings were obtained with a one-channel biomagnetometer SQUID in a magnetically shielded room.
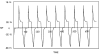
Results: Using the method of x2-fitting it was found that the MEG amplitudes in epileptic patients and normal subjects had Poisson and Gauss distributions respectively. The Poisson connectivity derived from the theoretical neural model represents the state of epilepsy, whereas the Gauss connectivity represents normal behavior. The MEG data obtained from epileptic areas had higher amplitudes than the MEG from normal regions and were comparable with the theoretical magnetic fields from Poisson and Gauss distributions. Furthermore, the magnetic field derived from the theoretical model had amplitudes in the same order as the recorded MEG from the 20 participants.
Conclusion: The approximation of the theoretical neural net model with real MEG data provides information about the structure of the brain function in epileptic and normal states encouraging further studies to be conducted.
Figures
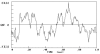

 = 15, ha = 0; mb = 0.2, θb = 4,
= 15, ha = 0; mb = 0.2, θb = 4,  = 192, hb = 0.01; mc = 0.1, θc = 3,
= 192, hb = 0.01; mc = 0.1, θc = 3,  = 34, hc = 0.01; md = 0.1, θd = 3,
= 34, hc = 0.01; md = 0.1, θd = 3,  = 32, hd = 0; K± = 1.
= 32, hd = 0; K± = 1.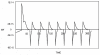
 = 14, ha = 0; mb = 0.08, θb = 4,
= 14, ha = 0; mb = 0.08, θb = 4,  = 240, hb = 0.02; mc = 0.02, θc = 4,
= 240, hb = 0.02; mc = 0.02, θc = 4,  = 400, hc = 0.0; md = 0.1, θd = 4,
= 400, hc = 0.0; md = 0.1, θd = 4,  = 337, hd = 0; me = 0.1, θe = 4,
= 337, hd = 0; me = 0.1, θe = 4,  = 294, he = 0.03; K± = 1.
= 294, he = 0.03; K± = 1.Similar articles
-
Alpha, delta and theta rhythms in a neural net model. Comparison with MEG data.J Theor Biol. 2016 Jan 7;388:11-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.10.005. Epub 2015 Oct 17. J Theor Biol. 2016. PMID: 26484893
-
State dependent properties of epileptic brain networks: comparative graph-theoretical analyses of simultaneously recorded EEG and MEG.Clin Neurophysiol. 2010 Feb;121(2):172-85. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2009.10.013. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Clin Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20045375
-
Magnetoencephalography for localizing and characterizing the epileptic focus.Handb Clin Neurol. 2019;160:203-214. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64032-1.00013-8. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31277848 Review.
-
MEG as a Medical Diagnostic Tool in the Greek Population.Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2015;58(3):71-8. doi: 10.14712/18059694.2015.100. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2015. PMID: 26686946 Review.
-
[Magnetoencephalographic localization of epileptic foci using a 37-channel biomagnetometer].No To Shinkei. 1991 Nov;43(11):1067-74. No To Shinkei. 1991. PMID: 1799513 Japanese.
Cited by
-
Use of genetic programming, logistic regression, and artificial neural nets to predict readmission after coronary artery bypass surgery.J Clin Monit Comput. 2013 Aug;27(4):455-64. doi: 10.1007/s10877-013-9444-7. Epub 2013 Mar 16. J Clin Monit Comput. 2013. PMID: 23504197
References
-
- Volkmann J, Joliot M, Mogilner A, Ioannides AA, Lado F, Fazzini E, Ribary U, Llinas R. Central motor loop oscillations in parkinsonian resting tremor revealed by magnetoencephalography. Neurol. 1996;46:1359–1370. - PubMed
-
- Anninos PA, Beek B, Csermely TJ, Harth EM, Pertile G. Dynamics of neural structures. J Theor Biol. 1970;26:121–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

