Novel type I interferon IL-28A suppresses hepatitis C viral RNA replication
- PMID: 16146571
- PMCID: PMC1232870
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-2-80
Novel type I interferon IL-28A suppresses hepatitis C viral RNA replication
Abstract
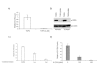
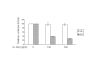
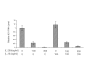
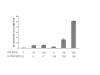
Interferon alpha (IFN-alpha)-based therapy is the currently approved treatment for chronic hepatitis C viral infection. The sustained antiviral response rate is approximately 50% for genotype-1 infection. The major challenge to the HCV community is to improve antiviral efficacy and to reduce the side effects typically seen in IFNalpha-based therapy. One of the strategies is to identify new interferons, which may have better efficacy and less undesirable side effects. In this report, we examined the role of IL-28A (IFN lambda2), a novel type I IFN, in suppression of human hepatitis C viral RNA replication. We have cloned both the human genomic DNA and cDNA of IL-28A, and evaluated their biological activity using HCV RNA replicon cell culture system. The results show that IL-28A effectively inhibits HCV subgenomic RNA replication in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment of human hepatoma cells with IL-28A activates the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and induces the expression of some interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), such as 6-16 and 1-8U. We also demonstrate that IL-28A induces expression of HLA class I antigens in human hepatoma cells. Moreover, IL-28A appears to specifically suppress HCV IRES-mediated translation. Although IL-28A receptor shares one subunit with the IL-10 receptor, IL-10 treatment has no detectable effect on IL-28A-induced antiviral activity. Interestingly, IL-28A can synergistically enhance IFNalpha antiviral efficacy. Our results suggest that IL-28A antiviral activity is associated with the activation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and expression of ISGs. The effectiveness of IL-28A antiviral activity and its synergistic effect on IFN-alpha indicate that IL-28A may be potentially used to treat HCV chronic infection.
Figures




Similar articles
-
IL28B inhibits hepatitis C virus replication through the JAK-STAT pathway.J Hepatol. 2011 Aug;55(2):289-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.11.019. Epub 2010 Dec 13. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21147189 Free PMC article.
-
Type III Interferon Induces Distinct SOCS1 Expression Pattern that Contributes to Delayed but Prolonged Activation of Jak/STAT Signaling Pathway: Implications for Treatment Non-Response in HCV Patients.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 20;10(7):e0133800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133800. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26193702 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-λ Inhibits MiR-122 Transcription through a Stat3-HNF4α Inflammatory Feedback Loop in an IFN-α Resistant HCV Cell Culture System.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0141655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141655. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26657215 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the molecular mechanism(s) of hepatitis C virus (HCV) induced interferon resistance.Infect Genet Evol. 2013 Oct;19:113-9. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2013.06.025. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Infect Genet Evol. 2013. PMID: 23831932 Review.
-
Interferons and hepatitis C virus.Swiss Med Wkly. 2012 May 9;142:w13586. doi: 10.4414/smw.2012.13586. eCollection 2012. Swiss Med Wkly. 2012. PMID: 22573217 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Cell Profiling of IFN-λ Response Shows pDCs Express Highest Level of IFN-λR1 and Are Directly Responsive via the JAK-STAT Pathway.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016 Dec;36(12):671-680. doi: 10.1089/jir.2015.0169. Epub 2016 Sep 12. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016. PMID: 27617757 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid inducible gene-I (RIG-I) signaling of hepatic stellate cells inhibits hepatitis C virus replication in hepatocytes.Innate Immun. 2013;19(2):193-202. doi: 10.1177/1753425912460414. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Innate Immun. 2013. PMID: 23060457 Free PMC article.
-
IFN-λ exerts opposing effects on T cell responses depending on the chronicity of the virus infection.J Immunol. 2014 Apr 15;192(8):3596-606. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301705. Epub 2014 Mar 19. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24646741 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of IFN-λ genes in hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocytes via IRF-3·IRF-7·NF-κB complex.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 21;289(8):5310-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.536102. Epub 2014 Jan 2. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24385435 Free PMC article.
-
Viral induction of the zinc finger antiviral protein is IRF3-dependent but NF-kappaB-independent.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 26;285(9):6080-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.054486. Epub 2010 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20048147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brassard DL, Grace MJ, Bordens RW. Interferon-alpha as an immunotherapeutic protein. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;71:565–581. - PubMed
-
- Sheppard P, Kindsvogel W, Xu W, Henderson K, Schlutsmeyer S, Whitmore TE, Kuestner R, Garrigues U, Birks C, Roraback J, Ostrander C, Dong D, Shin J, Presnell S, Fox B, Haldeman B, Cooper E, Taft D, Gilbert T, Grant FJ, Tackett M, Krivan W, McKnight G, Clegg C, Foster D, Klucher KM. IL-28, IL-29 and their class II cytokine receptor IL-28R. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:63–68. doi: 10.1038/ni873. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Baig E, Fish EN. Diversity and relatedness among the type I interferons. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004;24:687–698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

