Changes in laminin isoforms associated with brain tumor invasion and angiogenesis
- PMID: 16146715
- PMCID: PMC3506377
- DOI: 10.2741/1781
Changes in laminin isoforms associated with brain tumor invasion and angiogenesis
Abstract
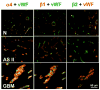
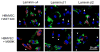
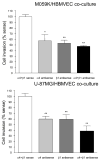
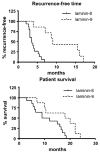
Laminins are the major constituents of blood vessel basement membranes (BMs). Each laminin is a trimer consisting of three assembled polypeptide chains, alpha, beta and gamma. More than 15 laminin isoforms are known to date and the expression of specific isoforms may change in certain pathological conditions. Here we show that during progression of glial tumors laminin-9 (alpha4beta2gamma1) is switched to laminin-8 (alpha4beta1gamma1), which is dramatically increased in glial brain tumors. Laminin-8 overproduction by glial tumor cells facilitates spread of glioma. Brain tumors with laminin-8 overexpression recur faster after standard treatment and patients have shorter survival time. Laminin-8 may be thus used as a predictor of tumor recurrence, patient survival and as a potential molecular target for glioma therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Shapiro WR, Shapiro JR. Biology and treatment of malignant glioma. Oncology. 1998;12:233–240. - PubMed
-
- Gonzales MF. Classification and pathogenesis of brain tumors. In: Kaye AH, Laws ER Jr, editors. Brain tumors. Churchill Livingstone; Edinburgh: 1997.
-
- Ljubimova JY, Khazenzon NM, Chen Z, Neyman YI, Turner L, Riedinger MS, Black KL. Gene array analysis of differentially expressed genes in human glial tumors. Int J Oncol. 2001;18:287–295. - PubMed
-
- Ljubimova JY, Lakhter AJ, Loksh A, Yong WH, Riedinger MS, Miner JH, Sorokin ML, Ljubimov AV, Black KL. Overexpression of α4 chain-containing laminins in human glial tumors identified by gene microarray analysis. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5601–5610. - PubMed
-
- Sehgal A. Molecular changes during the genesis of human gliomas. Semin Surg Oncol. 1998;14:3–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
