CD4+ regulatory cells as a potential immunotherapy
- PMID: 16147529
- PMCID: PMC1569534
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2005.1695
CD4+ regulatory cells as a potential immunotherapy
Abstract
CD4(+) regulatory T (T(R)) cells represent a unique lineage of thymically generated lymphocytes capable of powerfully suppressing immune responses. A large body of experimental data has now confirmed the key role played by these cells in the maintenance of self-tolerance. Increasingly, the importance of these cells is also being recognized in a host of other clinically relevant areas such as transplantation, tumour immunity, allergy and microbial immunity. Additionally, it is also possible to generate T(R) cells by using a variety of ex vivo experimental approaches. We will focus here on harnessing the suppressive abilities of both these families of regulatory cells and how this should give us access to a potent cell-based immunotherapy appropriate for clinical application.
Figures




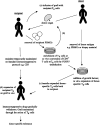
References
-
- Allegretta M, Nicklas J.A, Sriram S, Albertini R.J. T cells responsive to myelin basic protein in patients with multiple sclerosis. Science. 1990;247:718–721. - PubMed
-
- Almeida A.R, Legrand N, Papiernik M, Freitas A.A. Homeostasis of peripheral CD4+T cells: IL-2R alpha and IL-2 shape a population of regulatory cells that controls CD4+ T cell numbers. J. Immunol. 2002;169:4850–4860. - PubMed
-
- Andersson P.O, Olsson A, Wadenvik H. Reduced transforming growth factor-beta1 production by mononuclear cells from patients with active chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br. J. Haematol. 2002;116:862–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

