Investigating the SecY plug movement at the SecYEG translocation channel
- PMID: 16148946
- PMCID: PMC1276166
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600804
Investigating the SecY plug movement at the SecYEG translocation channel
Abstract
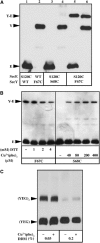
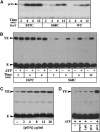
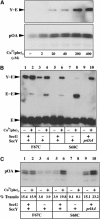
Protein translocation occurs across the energy-conserving bacterial membrane at the SecYEG channel. The crystal structure of the channel has revealed a possible mechanism for gating and opening. This study evaluates the plug hypothesis using cysteine crosslink experiments in combination with various allelic forms of the Sec complex. The results demonstrate that the SecY plug domain moves away from the center of the channel toward SecE during polypeptide translocation, and further show that the translocation-enhancing prlA3 mutation and SecG subunit change the properties of channel gating. Locking the plug in the open state preactivates the Sec complex, and a super-active translocase can be created when combined with the prlA4 mutation located in the pore of the channel. Dimerization of the Sec complex, which is essential for translocase activity, relocates the plug toward the open position. We propose that oligomerization may result in SecYEG cooperative interactions important to prime the translocon function.
Figures

References
-
- Beckmann R, Spahn CM, Eswar N, Helmers J, Penczek PA, Sali A, Frank J, Blobel G (2001) Architecture of the protein-conducting channel associated with the translating 80S ribosome. Cell 107: 361–372 - PubMed
-
- Breyton C, Haase W, Rapoport TA, Kuhlbrandt W, Collinson I (2002) Three-dimensional structure of the bacterial protein-translocation complex SecYEG. Nature 418: 662–665 - PubMed
-
- Cao TB, Saier MH (2003) The general protein secretory pathway: phylogenetic analyses leading to evolutionary conclusions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1609: 115–125 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

