Characterization of a multicopper oxidase gene from Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 16151171
- PMCID: PMC1214694
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.9.5650-5653.2005
Characterization of a multicopper oxidase gene from Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
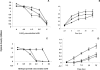
A multicopper oxidase gene from Staphylococcus aureus was cloned and overexpressed. Purified recombinant multicopper oxidase oxidized the substrate 3,3'-dimethoxybenzidine in the presence of copper. Disruption of mco showed copper sensitivity and H(2)O(2) resistance, suggesting roles for mco in copper homeostasis and oxidative stress response. Northern blot analysis showed copper-induced mco transcription.
Figures
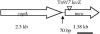

References
-
- Askwith, C. C., and J. Kaplan. 1998. Site-directed mutagenesis of the yeast multicopper oxidase Fet3p. J. Biol. Chem. 273:22415-22419. - PubMed
-
- de Silva, D., S. Davis-Kaplan, J. Fergestad, and J. Kaplan. 1977. Purification and characterization of Fet3 protein, a yeast homologue of ceruloplasmin. J. Biol. Chem. 272:14208-14213. - PubMed
-
- Eck, R., S. Hundt, A. Hartl, E. Roemer, and W. Kunkel. 1999. A multicopper oxidase gene from Candida albicans: cloning, characterization and disruption. Microbiology 145:2415-2422. - PubMed
-
- Feldman, S. L., J. S. V. Hunter, A. Zgirski, V. M. Chidambaram, and E. Frieden. 1982. Comparison of the catalytic oxidation of cysteine and o-dianisidine by cupric ion and ceruloplasmin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 17:51-60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

