Functional characterization and expression of endothelin receptors in rat carotid artery: involvement of nitric oxide, a vasodilator prostanoid and the opening of K+ channels in ETB-induced relaxation
- PMID: 16151434
- PMCID: PMC1751214
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706388
Functional characterization and expression of endothelin receptors in rat carotid artery: involvement of nitric oxide, a vasodilator prostanoid and the opening of K+ channels in ETB-induced relaxation
Abstract
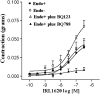
We aimed to functionally characterize endothelin (ET) receptors in the rat carotid artery. mRNA and protein expressions of both ETA and ETB receptors, evaluated by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western immunoblotting, were detected in carotid segments. Immunohistochemical assays showed that ETB receptors are expressed in the endothelium and smooth muscle cells, while ETA receptors are expressed only in the smooth muscle cells. In endothelium-denuded vessels, levels of ETB receptor mRNA were reduced. Vascular reactivity experiments, using standard muscle bath procedures, showed that ET-1 induces contraction in endothelium-intact and -denuded carotid rings in a concentration-dependent manner. Endothelial removal enhanced ET-1-induced contraction. BQ123 and BQ788, selective antagonists for ETA and ETB receptors, respectively, produced concentration-dependent rightward displacements of the ET-1 concentration-response curves. IRL1620, a selective agonist for ETB receptors, induced a slight vasoconstriction that was abolished by BQ788, but not affected by BQ123. IRL1620-induced contraction was augmented after endothelium removal. ET-1 concentration dependently relaxed phenylephrine-precontracted rings with intact endothelium. The relaxation was augmented in the presence of BQ123, reduced in the presence of BQ788 and completely abolished after endothelium removal. IRL1620 induced vasorelaxation that was abolished by BQ788 and endothelium removal, but not affected by BQ123. Preincubation of intact rings with N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ), indomethacin or tetraethylammonium (TEA) reduced IRL1620-induced relaxation. The combination of L-NAME, indomethacin and TEA completely abolished IRL1620-induced relaxation while sulfaphenazole did not affect this response. 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), but not apamin, glibenclamide or charybdotoxin, reduced IRL1620-induced relaxation. The major finding of this work is that it firstly demonstrated functionally the existence of both ETA and ETB vasoconstrictor receptors located on the smooth muscle of rat carotid arteries and endothelial ETB receptors that mediated vasorelaxation via NO-cGMP pathway, vasodilator cyclooxygenase product(s) and the activation of voltage-dependent K+ channels.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Ethanol consumption enhances endothelin-1-induced contraction in the isolated rat carotid.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Aug;318(2):819-27. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.103010. Epub 2006 May 1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006. PMID: 16651399
-
Pharmacological characterisation of the mechanisms underlying the relaxant effect of adrenomedullin in the rat carotid artery.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014 Dec;66(12):1734-46. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12299. Epub 2014 Aug 13. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25117796
-
Endothelium-dependent relaxation counteracting the contractile action of endothelin-1 is partly due to ETB receptor activation.Res Exp Med (Berl). 1997;196(6):327-37. doi: 10.1007/BF02576857. Res Exp Med (Berl). 1997. PMID: 9089881
-
Endothelin and endothelin antagonists in hypertension.J Hypertens. 1998 Dec;16(12 Pt 2):1891-5. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199816121-00007. J Hypertens. 1998. PMID: 9886874 Review.
-
Endothelium-derived endothelin-1.Pflugers Arch. 2010 May;459(6):951-8. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0763-y. Epub 2009 Dec 5. Pflugers Arch. 2010. PMID: 19967386 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Flow-mediated dilation stimulated by sustained increases in shear stress: a useful tool for assessing endothelial function in humans?Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Mar 1;314(3):H508-H520. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00534.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29167121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Local antinociception induced by endothelin-1 in the hairy skin of the rat's back.J Pain. 2009 Jul;10(7):702-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2008.12.005. J Pain. 2009. PMID: 19559389 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-Induced Modulation of Angiotensin II Responses in Femoral Veins From 2-Kidney-1-Clip Hypertensive Rats.Front Physiol. 2021 Apr 7;12:620438. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.620438. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33897446 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic ethanol intake modulates vascular levels of endothelin-1 receptor and enhances the pressor response to endothelin-1 in anaesthetized rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Jul;154(5):971-81. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.157. Epub 2008 May 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18469849 Free PMC article.
-
The role of prostaglandin and antioxidant availability in recovery from forearm ischemia-reperfusion injury in humans.J Hypertens. 2014 Feb;32(2):339-51. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000033. J Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24296519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ARCHER S.L., GRAGASIN F.S., WU X., WANG S., McMURTRY S., KIM D.H., PLATONOV M., KOSHAL A., HASHIMOTO K., CAMPBELL W.B., FALCK J.R., MICHELAKIS E.D. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in human internal mammary artery is 11,12-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid and causes relaxation by activating smooth muscle BKCa channels. Circulation. 2003;107:769–776. - PubMed
-
- AUGUET M., DELLAFLOTTE S., CHABRIER P.E., BRAQUET P. Characterization of endothelin receptors mediating contraction and relaxation in rabbit saphenous artery and vein. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1993;71:818–823. - PubMed
-
- BUSSEMAKER E., POPP R., FISSLTHALER B., LARSON C.M., FLEMING I., BUSSE R., BRANDES R.P. Aged spontaneously hypertensive rats exhibit a selective loss of EDHF-mediated relaxation in the renal artery. Hypertension. 2003;42:562–568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

