Adiponectin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through AMPK- and COX-2-dependent mechanisms
- PMID: 16155579
- PMCID: PMC2828682
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1295
Adiponectin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through AMPK- and COX-2-dependent mechanisms
Abstract
Obesity-related disorders are associated with the development of ischemic heart disease. Adiponectin is a circulating adipose-derived cytokine that is downregulated in obese individuals and after myocardial infarction. Here, we examine the role of adiponectin in myocardial remodeling in response to acute injury. Ischemia-reperfusion in adiponectin-deficient (APN-KO) mice resulted in increased myocardial infarct size, myocardial apoptosis and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha expression compared with wild-type mice. Administration of adiponectin diminished infarct size, apoptosis and TNF-alpha production in both APN-KO and wild-type mice. In cultured cardiac cells, adiponectin inhibited apoptosis and TNF-alpha production. Dominant negative AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) reversed the inhibitory effects of adiponectin on apoptosis but had no effect on the suppressive effect of adiponectin on TNF-alpha production. Adiponectin induced cyclooxygenase (COX)-2-dependent synthesis of prostaglandin E(2) in cardiac cells, and COX-2 inhibition reversed the inhibitory effects of adiponectin on TNF-alpha production and infarct size. These data suggest that adiponectin protects the heart from ischemia-reperfusion injury through both AMPK- and COX-2-dependent mechanisms.
Figures
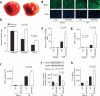
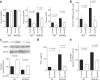
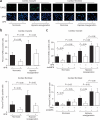
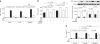
Comment in
-
Fat, keeping the heart healthy?Nat Med. 2005 Oct;11(10):1048-9. doi: 10.1038/nm1005-1048. Nat Med. 2005. PMID: 16211035 No abstract available.
References
-
- Eisenberg MS, Mengert TJ. Cardiac resuscitation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:1304–1313. - PubMed
-
- Rogers WJ, et al. Temporal trends in the treatment of over 1.5 million patients with myocardial infarction in the US from 1990 through 1999: the National Registry of Myocardial Infarction 1, 2 and 3. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000;36:2056–2063. - PubMed
-
- Wolk R, Berger P, Lennon RJ, Brilakis ES, Somers VK. Body mass index: a risk factor for unstable angina and myocardial infarction in patients with angiographically confirmed coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2003;108:2206–2211. - PubMed
-
- Orlander PR, et al. The relation of diabetes to the severity of acute myocardial infarction and post-myocardial infarction survival in Mexican-Americans and non-Hispanic whites. The Corpus Christi Heart Project. Diabetes. 1994;43:897–902. - PubMed
-
- Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, Baldini G, Lodish HF. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:26746–26749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

