Carbohydrate specificity of an insecticidal lectin isolated from the leaves of Glechoma hederacea (ground ivy) towards mammalian glycoconjugates
- PMID: 16156719
- PMCID: PMC1383692
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051162
Carbohydrate specificity of an insecticidal lectin isolated from the leaves of Glechoma hederacea (ground ivy) towards mammalian glycoconjugates
Abstract
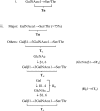
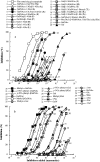
Preliminary studies indicated that the potent insecticidal lectin, Gleheda, from the leaves of Glechoma hederacea (ground ivy) preferentially agglutinates human erythrocytes carrying the Tn (GalNAcalpha1-Ser/Thr) antigen. However, no details have been reported yet with respect to the fine specificity of the lectin. To corroborate the molecular basis of the insecticidal activity and physiological function of Gleheda, it is necessary to identify the recognition factors that are involved in the Gleheda-glycotope interaction. In the present study, the requirement of high-density multivalent carbohydrate structural units for Gleheda binding and a fine-affinity profile were evaluated using ELLSA (enzyme-linked lectinosorbent assay) with our extended glycan/ligand collections, a glycan array and molecular modelling. From the results, we concluded that a high-density of exposed multivalent Tn-containing glycoproteins (natural armadillo and asialo ovine salivary glycoproteins) were the most potent factors for Gleheda binding. They were, on a nanogram basis, 6.5x10(5), 1.5x10(4) and 3.1x10(3) times more active than univalent Gal (galactose), GalNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine) and Tn respectively. Among mono- and oligo-saccharides examined, simple clustered Tn (molecular mass <3000 Da) from ovine salivary glycoprotein was the best, being 37.5 and 1.7x10(3) times better than GalNAc and Gal respectively. GalNAc glycosides were significantly more active than Gal glycosides, indicating that the N-acetamido group at C-2 plays an important role in Gleheda binding. The results of glycan array support the conclusions drawn with respect to the specificity of Gleheda based on the ELLSA assays. These findings combined with the results of the molecular modelling and docking indicate the occurrence of a primary GalNAcalpha1-binding site in the Gleheda monomer. However, the extraordinary binding feature of Gleheda for glycoproteins demonstrates the importance of affinity enhancement by high-density multivalent glycotopes in the ligand-lectin interactions in biological processes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lectinochemical studies on the glyco-recognition factors of a Tn (GalNAcalpha1-->Ser/Thr) specific lectin isolated from the seeds of Salvia sclarea.J Biomed Sci. 2005;12(1):167-84. doi: 10.1007/s11373-004-8180-x. J Biomed Sci. 2005. PMID: 15864748
-
The Tn antigen-specific lectin from ground ivy is an insecticidal protein with an unusual physiology.Plant Physiol. 2003 Jul;132(3):1322-34. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.023853. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12857814 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition profile of Morus nigra agglutinin (Morniga G) expressed by monomeric ligands, simple clusters and mammalian polyvalent glycotopes.Mol Immunol. 2007 Jan;44(4):451-62. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2006.02.017. Epub 2006 Apr 3. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 16581130
-
Expression of binding properties of Gal/GalNAc reactive lectins by mammalian glycotopes (an updated report).Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001;491:55-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-1267-7_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001. PMID: 14533789 Review.
-
Lectins and ELLSA as powerful tools for glycoconjugate recognition analyses.Glycoconj J. 2019 Apr;36(2):175-183. doi: 10.1007/s10719-019-09865-3. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Glycoconj J. 2019. PMID: 30993518 Review.
Cited by
-
A Tn antigen binding lectin from Myrsine coriacea displays toxicity in human cancer cell lines.J Nat Med. 2013 Apr;67(2):247-54. doi: 10.1007/s11418-012-0671-x. Epub 2012 May 30. J Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 22645079
-
The liverwort Marchantia polymorpha expresses orthologs of the fungal Agaricus bisporus agglutinin family.Plant Physiol. 2007 Jun;144(2):637-47. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.087437. Epub 2006 Oct 13. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17041032 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Protein O-GalNAcylation: Method Development and Disease Implication.ACS Omega. 2023 May 24;8(22):19223-19236. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01653. eCollection 2023 Jun 6. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37305274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medicinal Plants of the Family Lamiaceae in Pain Therapy: A Review.Pain Res Manag. 2018 May 8;2018:7801543. doi: 10.1155/2018/7801543. eCollection 2018. Pain Res Manag. 2018. PMID: 29854039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant Lectins Targeting O-Glycans at the Cell Surface as Tools for Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jun 9;18(6):1232. doi: 10.3390/ijms18061232. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28598369 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang W., Peumans W. J., Rougé P., Rossi C., Proost P., Chen J., Van Damme E. J. M. Leaves of the Lamiaceae species Glechoma hederacea (ground ivy) contain a lectin that is structurally and evolutionary related to the legume lectins. Plant J. 2003;33:293–304. - PubMed
-
- Springer G. F. T and Tn, general carcinoma autoantigens. Science. 1984;24:1189–1260. - PubMed
-
- Springer G. F. Immunoreactive T and Tn epitopes in cancer diagnosis, prognosis, and immunotherapy. J. Mol. Med. 1997;75:594–602. - PubMed
-
- Itzkowitz S. H., Bloom E. J., Kokal W. A., Modin G., Hakomori S. I., Kim Y. S. Sialosyl-Tn: a novel mucin antigen associated with prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Cancer. 1990;66:1960–1966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

