Translation elongation factor eEF1A2 is a potential oncoprotein that is overexpressed in two-thirds of breast tumours
- PMID: 16156888
- PMCID: PMC1236916
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-113
Translation elongation factor eEF1A2 is a potential oncoprotein that is overexpressed in two-thirds of breast tumours
Abstract
Background: The tissue-specific translation elongation factor eEF1A2 was recently shown to be a potential oncogene that is overexpressed in ovarian cancer. Although there is no direct evidence for an involvement of eEF1A2 in breast cancer, the genomic region to which EEF1A2 maps, 20q13, is frequently amplified in breast tumours. We therefore sought to establish whether eEF1A2 expression might be upregulated in breast cancer.
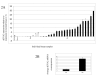
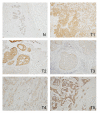
Methods: eEF1A2 is highly similar (98%) to the near-ubiquitously expressed eEF1A1 (formerly known as EF1-alpha) making analysis with commercial antibodies difficult. We have developed specific anti-eEF1A2 antibodies and used them in immunohistochemical analyses of tumour samples. We report the novel finding that although eEF1A2 is barely detectable in normal breast it is moderately to strongly expressed in two-thirds of breast tumours. This overexpression is strongly associated with estrogen receptor positivity.
Conclusion: eEF1A2 should be considered as a putative oncogene in breast cancer that may be a useful diagnostic marker and therapeutic target for a high proportion of breast tumours. The oncogenicity of eEF1A2 may be related to its role in protein synthesis or to its potential non-canonical functions in cytoskeletal remodelling or apoptosis.
Figures

References
-
- Ann DK, Moutsatsos IK, Nakamura T, Lin HH, Mao PL, Lee MJ, Chin S, Liem RK, Wang E. Isolation and characterization of the rat chromosomal gene for a polypeptide (pS1) antigenically related to statin. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:10429–10437. - PubMed
-
- Knudsen SM, Frydenberg J, Clark BF, Leffers H. Tissue-dependent variation in the expression of elongation factor-1 alpha isoforms: isolation and characterisation of a cDNA encoding a novel variant of human elongation-factor 1 alpha. Eur J Biochem. 1993;215:549–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18064.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Francoeur AM, Liu S, Wang E. Tissue-specific expression in mammalian brain, heart, and muscle of S1, a member of the elongation factor-1 alpha gene family. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:24064–24068. - PubMed
-
- Chambers DM, Peters J, Abbott CM. The lethal mutation of the mouse wasted (wst) is a deletion that abolishes expression of a tissue-specific isoform of translation elongation factor 1alpha, encoded by the Eef1a2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:4463–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4463. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

