Rapid single nucleotide polymorphism mapping in C. elegans
- PMID: 16156901
- PMCID: PMC1242227
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-118
Rapid single nucleotide polymorphism mapping in C. elegans
Abstract
Background: In C. elegans, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can function as silent genetic markers, with applications ranging from classical two- and three-factor mapping to measuring recombination across whole chromosomes.
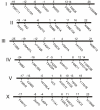
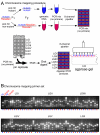
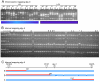
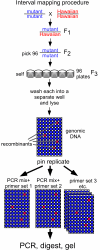
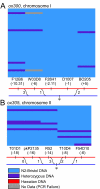
Results: Here, we describe a set of 48 primer pairs that flank SNPs evenly spaced across the C. elegans genome and that work under identical PCR conditions. Each SNP in this set alters a DraI site, enabling rapid and parallel scoring. We describe a procedure using these reagents to quickly and reliably map mutations. We show that these techniques correctly map a known gene, dpy-5. We then use these techniques to map mutations in an uncharacterized strain, and show that its behavioral phenotype can be simultaneously mapped to three loci.
Conclusion: Together, the reagents and methods described represent a significant advance in the accurate, rapid and inexpensive mapping of genes in C. elegans.
Figures
References
-
- C. elegans Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Data http://genomeold.wustl.edu/projects/celegans/index.php?snp=1
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

