ERalpha and ERbeta expression and transcriptional activity are differentially regulated by HDAC inhibitors
- PMID: 16158045
- PMCID: PMC2034758
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209102
ERalpha and ERbeta expression and transcriptional activity are differentially regulated by HDAC inhibitors
Abstract
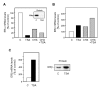
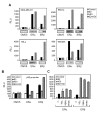
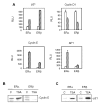
The proliferative action of ERalpha largely accounts for the carcinogenic activity of estrogens. By contrast, recent data show that ERbeta displays tumor-suppressor properties, thus supporting the interest to identify compounds that could increase its activity. Here, we show that histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI) upregulated ERbeta protein levels, whereas it decreased ERalpha expression. Part of this regulation took place at the mRNA level through a mechanism independent of de novo protein synthesis. In addition, we found that, in various cancer cells, the treatment with different HDI enhanced the ligand-dependent activity of ERbeta more strongly than that of ERalpha. On the other hand, in MDA-MB231 and HeLa cells, the expression of ERs modified the transcriptional response to HDI. The use of deletion mutants of both receptors demonstrated that AF1 domain of the receptors was required. Finally, we show that ERbeta expression led to a dramatic increased in the antiproliferative activity of HDI, which correlated with a modification of the transcription of genes involved in cell cycle control by HDI. Altogether, these data demonstrate that the interference of ERbeta and HDAC on the control of transcription and cell proliferation constitute a promising approach for cancer therapy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Artemisinin selectively decreases functional levels of estrogen receptor-alpha and ablates estrogen-induced proliferation in human breast cancer cells.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Dec;29(12):2252-8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn214. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18784357 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition and estrogen receptor alpha levels modulate the transcriptional activity of partial antiestrogens.J Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Apr;32(2):583-94. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0320583. J Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15072561
-
Raloxifene induces cell death and inhibits proliferation through multiple signaling pathways in prostate cancer cells expressing different levels of estrogen receptor α and β.J Cell Physiol. 2011 May;226(5):1334-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22461. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20945400
-
Harmful effect of ERβ on BCRP-mediated drug resistance and cell proliferation in ERα/PR-negative breast cancer.FEBS J. 2013 Dec;280(23):6128-40. doi: 10.1111/febs.12533. Epub 2013 Oct 8. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 24103091
-
Estrogen Receptor β as a Possible Double-Edged Sword Molecule in Breast Cancer: A Mechanism of Alteration of Its Role by Exposure to Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals.Biol Pharm Bull. 2021;44(11):1594-1597. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b21-00468. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 34719637 Review.
Cited by
-
The Synergistic Effect of Proanthocyanidin and HDAC Inhibitor Inhibit Breast Cancer Cell Growth and Promote Apoptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 22;24(13):10476. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310476. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445654 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors in recent clinical trials for cancer therapy.Clin Epigenetics. 2010 Dec;1(3-4):117-136. doi: 10.1007/s13148-010-0012-4. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Clin Epigenetics. 2010. PMID: 21258646 Free PMC article.
-
The silent estrogen receptor--can we make it speak?Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Mar 15;8(6):485-96. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.6.7582. Epub 2009 Mar 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19411863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hdac3 deficiency limits periosteal reaction associated with Western diet feeding in female mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Sep;28(17):e70081. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70081. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39261913 Free PMC article.
-
The role of histone modifications and variants in regulating gene expression in breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010 Mar;15(1):19-33. doi: 10.1007/s10911-010-9167-z. Epub 2010 Feb 4. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20131086 Review.
References
-
- Campbell-Thompson M, Lynch IJ, Bhardwaj B. Cancer Res. 2001;61:632–40. - PubMed
-
- Cheng J, Lee EJ, Madison LD, Lazennec G. FEBS Lett. 2004;566:169–72. - PubMed
-
- Cohen LA, Amin S, Marks PA, Rifkind RA, Desai D, Richon VM. Anticancer Res. 1999;19:4999–5005. - PubMed
-
- Cowley SM, Parker MG. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1999;69:165–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

