The forkhead transcription factor Foxi1 directly activates the AE4 promoter
- PMID: 16159312
- PMCID: PMC1383686
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20051094
The forkhead transcription factor Foxi1 directly activates the AE4 promoter
Abstract
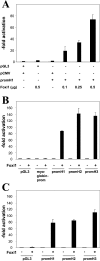
Intercalated cells are highly specialized cells within the renal collecting duct epithelium and play an important role in systemic acid-base homoeostasis. Whereas type A intercalated cells secrete protons via an apically localized H+-ATPase, type B intercalated cells secrete HCO3-. Type B intercalated cells specifically express the HCO3-/Cl- exchanger AE4 (anion exchanger 4), encoded by Slc4a9. Mice with a targeted disruption of the gene for the forkhead transcription factor Foxi1 display renal tubular acidosis due to an intercalated cell-differentiation defect. Collecting duct cells in these mice are characterized by the absence of inter-calated cell markers including AE4. To test whether Slc4a9 is a direct target gene of Foxi1, an AE4 promoter construct was generated for a cell-based reporter gene assay. Co-transfection with the Foxi1 cDNA resulted in an approx. 100-fold activation of the AE4 promoter construct. By truncating the AE4 promoter at the 5'-end, we demonstrate that a fragment of approx. 462 bp upstream of the transcription start point is sufficient to mediate activation by Foxi1. Sequence analysis of this region revealed at least eight potential binding sites for Foxi1 in both sense and antisense orientation. Only one element was bound by recombinant Foxi1 protein in bandshift assays. Mutation of this site abolished both binding in bandshift assays and transcriptional activation by co-transfection of Foxi1 in the reporter gene assay. We thus identify the AE4 promoter as a direct target of Foxi1.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The transcription factor Foxi1 promotes expression of V-ATPase and Gpr116 in M-1 cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Mar 1;324(3):F267-F273. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00272.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36603001 Free PMC article.
-
The murine AE4 promoter predominantly drives type B intercalated cell specific transcription.Histochem Cell Biol. 2009 Oct;132(4):405-12. doi: 10.1007/s00418-009-0614-0. Epub 2009 Jun 21. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19544066
-
Epididymal expression of the forkhead transcription factor Foxi1 is required for male fertility.EMBO J. 2006 Sep 6;25(17):4131-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601272. Epub 2006 Aug 24. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16932748 Free PMC article.
-
AE4 is a DIDS-sensitive Cl(-)/HCO(-)(3) exchanger in the basolateral membrane of the renal CCD and the SMG duct.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002 Oct;283(4):C1206-18. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00512.2001. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12225984
-
Novel functions of the anion exchanger AE4 (SLC4A9).Pflugers Arch. 2024 Apr;476(4):555-564. doi: 10.1007/s00424-023-02899-5. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Pflugers Arch. 2024. PMID: 38195948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The SLC4 family of bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) transporters.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Apr-Jun;34(2-3):159-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.10.008. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23506864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Foxi3 transcription factor activity is mediated by a C-terminal transactivation domain and regulated by the Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) complex.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 22;8(1):17249. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35390-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30467319 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor Foxi1 promotes expression of V-ATPase and Gpr116 in M-1 cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Mar 1;324(3):F267-F273. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00272.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36603001 Free PMC article.
-
FOXI3 pathogenic variants cause one form of craniofacial microsomia.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 11;14(1):2026. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37703-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37041148 Free PMC article.
-
FOXI1 expression in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and renal oncocytoma: a study of The Cancer Genome Atlas transcriptome-based outlier mining and immunohistochemistry.Virchows Arch. 2021 Apr;478(4):647-658. doi: 10.1007/s00428-020-02900-x. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Virchows Arch. 2021. PMID: 32812119
References
-
- Bouchard M. Transcriptional control of kidney development. Differentiation. 2004;72:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Wagner C. A., Geibel J. P. Acid-base transport in the collecting duct. J. Nephrol. 2002;15(Suppl. 5):S112–S127. - PubMed
-
- Brown D., Hirsch S., Gluck S. An H+-ATPase in opposite plasma membrane domains in kidney epithelial cell subpopulations. Nature (London) 1988;331:622–624. - PubMed
-
- Schuster V. L., Bonsib S. M., Jennings M. L. Two types of collecting duct mitochondria-rich (intercalated) cells: lectin and band 3 cytochemistry. Am. J. Physiol. 1986;251:C347–C355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

