Open-label treatment with citalopram in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a pilot study
- PMID: 16163399
- PMCID: PMC1192434
- DOI: 10.4088/pcc.v07n0404
Open-label treatment with citalopram in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: This open-label pilot study investigated whether the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) citalopram improves symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a functional gastrointestinal disorder with frequent psychiatric comorbidity.
Method: Fifteen patients meeting Rome I criteria for IBS were administered open-label citalopram (20-40 mg/day) for 12 weeks. The study was conducted from October 2000 to August 2001.
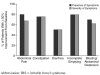
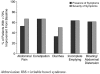
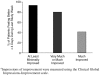
Results: Twelve (80%) of the 15 subjects reported a > or = 50% decrease in the presence of abdominal pain, 10 (67%) reported a > or = 50% reduction in the severity of the symptom, and 12 (80%) reported a > or = 50% reduction in the frequency of the symptom. Approximately one half of the patients met criteria for remission (> or = 70% improvement) of abdominal pain.
Conclusion: Results of this pilot study suggest that large controlled trials are needed to further evaluate the efficacy of SSRIs such as citalopram for the treatment of IBS.
Figures
References
-
- Lynn RB, Friedman LS. Irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1940–1945. - PubMed
-
- Talley NJ, Zinsmeister AR, and Van Dyke C. et al. Epidemiology of colonic symptoms and the irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1991 101:927–934. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell CM, Drossman DA. Survey of the AGA membership relating to patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gastroenterology. 1987;92:1282–1284. - PubMed
-
- Norton N. Functional bowel disorders survey. Participate. 1997;6:1–3.
-
- Read NW. ed. The neurotic bowel: a paradigm for the irritable bowel syndrome. In: Read NW, ed. Irritable Bowel Syndrome, New Insights Into Pathophysiology. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Scientific Publications. 1991 3–4.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous