Sodium pump alpha2 subunits control myogenic tone and blood pressure in mice
- PMID: 16166162
- PMCID: PMC1464198
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.091801
Sodium pump alpha2 subunits control myogenic tone and blood pressure in mice
Abstract
A key question in hypertension is: How is long-term blood pressure controlled? A clue is that chronic salt retention elevates an endogenous ouabain-like compound (EOLC) and induces salt-dependent hypertension mediated by Na(+)/Ca(2)(+) exchange (NCX). The precise mechanism, however, is unresolved. Here we study blood pressure and isolated small arteries of mice with reduced expression of Na(+) pump alpha1 (alpha1(+/-)) or alpha2 (alpha2(+/-)) catalytic subunits. Both low-dose ouabain (1-100 nm; inhibits only alpha2) and high-dose ouabain (> or =1 microm; inhibits alpha1) elevate myocyte Ca(2)(+) and constrict arteries from alpha1(+/-), as well as alpha2(+/-) and wild-type mice. Nevertheless, only mice with reduced alpha2 Na(+) pump activity (alpha2(+/-)), and not alpha1 (alpha1(+/-)), have elevated blood pressure. Also, isolated, pressurized arteries from alpha2(+/-), but not alpha1(+/-), have increased myogenic tone. Ouabain antagonists (PST 2238 and canrenone) and NCX blockers (SEA0400 and KB-R7943) normalize myogenic tone in ouabain-treated arteries. Only the NCX blockers normalize the elevated myogenic tone in alpha2(+/-) arteries because this tone is ouabain independent. All four agents are known to lower blood pressure in salt-dependent and ouabain-induced hypertension. Thus, chronically reduced alpha2 activity (alpha2(+/-) or chronic ouabain) apparently regulates myogenic tone and long-term blood pressure whereas reduced alpha1 activity (alpha1(+/-)) plays no persistent role: the in vivo changes in blood pressure reflect the in vitro changes in myogenic tone. Accordingly, in salt-dependent hypertension, EOLC probably increases vascular resistance and blood pressure by reducing alpha2 Na(+) pump activity and promoting Ca(2)(+) entry via NCX in myocytes.
Figures


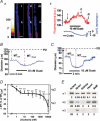






References
-
- Abarquez RF., Jr Digitalis in the treatment of hypertension. A preliminary report. Acta Med Philipp. 1967;3:161–170. - PubMed
-
- Arnon A, Hamlyn JM, Blaustein MP. Ouabain augments Ca2+ transients in arterial smooth muscle without raising cytosolic Na+ Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279:H679–H691. - PubMed
-
- Bagrov AY, Roukoyatkina NI, Pinaev AG, Dmitrieva RI, Fedorova OV. Effects of two endogenous Na+,K+-ATPase inhibitors, marinobufagenin and ouabain, on isolated rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995;274:151–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

