Chronic liver injury in rats and humans upregulates the novel enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme 2
- PMID: 16166274
- PMCID: PMC1774784
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2004.062398
Chronic liver injury in rats and humans upregulates the novel enzyme angiotensin converting enzyme 2
Abstract
Background: Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) 2 is a recently identified homologue of ACE that may counterregulate the actions of angiotensin (Ang) II by facilitating its breakdown to Ang 1-7. The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of cirrhosis but the role of ACE2 in liver disease is not known.
Aims: This study examined the effects of liver injury on ACE2 expression and activity in experimental hepatic fibrosis and human cirrhosis, and the effects of Ang 1-7 on vascular tone in cirrhotic rat aorta.
Methods: In sham operated and bile duct ligated (BDL) rats, quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction was used to assess hepatic ACE2 mRNA, and western blotting and immunohistochemistry to quantify and localise ACE2 protein. ACE2 activity was quantified by quenched fluorescent substrate assay. Similar studies were performed in normal human liver and in hepatitis C cirrhosis.
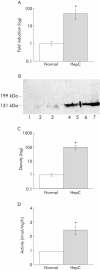
Results: ACE2 mRNA was detectable at low levels in rat liver and increased following BDL (363-fold; p < 0.01). ACE2 protein increased after BDL (23.5-fold; p < 0.05) as did ACE2 activity (fourfold; p < 0.05). In human cirrhotic liver, gene (>30-fold), protein expression (97-fold), and activity of ACE2 (2.4 fold) were increased compared with controls (all p < 0.01). In healthy livers, ACE2 was confined to endothelial cells, occasional bile ducts, and perivenular hepatocytes but in both BDL and human cirrhosis there was widespread parenchymal expression of ACE2 protein. Exposure of cultured human hepatocytes to hypoxia led to increased ACE2 expression. In preconstricted rat aorta, Ang 1-7 alone did not affect vascular tone but it significantly enhanced acetylcholine mediated vasodilatation in cirrhotic vessels.
Conclusions: ACE2 expression is significantly increased in liver injury in both humans and rat, possibly in response to increasing hepatocellular hypoxia, and may modulate RAS activity in cirrhosis.
Figures




References
-
- Paizis G, Gilbert RE, Cooper ME, et al. Effect of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade on experimental hepatic fibrogenesis. J Hepatol 2001;35:376–85. - PubMed
-
- Paizis G, Cooper ME, Schembri JM, et al. Up-regulation of components of the renin-angiotensin system in the bile duct-ligated rat liver. Gastroenterology 2002;123:1667–76. - PubMed
-
- Jonsson JR, Clouston AD, Ando Y, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition attenuates the progression of rat hepatic fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2001;121:148–55. - PubMed
-
- Bataller R, Sancho-Bru P, Gines P, et al. Activated human hepatic stellate cells express the renin-angiotensin system and synthesize angiotensin II. Gastroenterology 2003;125:117–25. - PubMed
-
- Helmy A, Jalan R, Newby DE, et al. Role of angiotensin II in regulation of basal and sympathetically stimulated vascular tone in early and advanced cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2000;118:565–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
