Addition of 5-fluorouracil to doxorubicin-paclitaxel sequence increases caspase-dependent apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines
- PMID: 16168113
- PMCID: PMC1242133
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr1274
Addition of 5-fluorouracil to doxorubicin-paclitaxel sequence increases caspase-dependent apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of the study was to evaluate the activity of a combination of doxorubicin (Dox), paclitaxel (Pacl) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), to define the most effective schedule, and to investigate the mechanisms of action in human breast cancer cells.
Methods: The study was performed on MCF-7 and BRC-230 cell lines. The cytotoxic activity was evaluated by sulphorhodamine B assay and the type of drug interaction was assessed by the median effect principle. Cell cycle perturbation and apoptosis were evaluated by flow cytometry, and apoptosis-related marker (p53, bcl-2, bax, p21), caspase and thymidylate synthase (TS) expression were assessed by western blot.
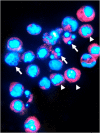
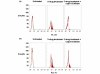
Results: 5-FU, used as a single agent, exerted a low cytotoxic activity in both cell lines. The Dox-->Pacl sequence produced a synergistic cytocidal effect and enhanced the efficacy of subsequent exposure to 5-FU in both cell lines. Specifically, the Dox-->Pacl sequence blocked cells in the G2-M phase, and the addition of 5-FU forced the cells to progress through the cell cycle or killed them. Furthermore, Dox-->Pacl pretreatment produced a significant reduction in basal TS expression in both cell lines, probably favoring the increase in 5-FU activity. The sequence Dox-->Pacl-->48-h washout-->5-FU produced a synergistic and highly schedule-dependent interaction (combination index < 1), resulting in an induction of apoptosis in both experimental models regardless of hormonal, p53, bcl-2 or bax status. Apoptosis in MCF-7 cells was induced through caspase-9 activation and anti-apoptosis-inducing factor hyperexpression. In the BRC-230 cell line, the apoptotic process was triggered only by a caspase-dependent mechanism. In particular, at the end of the three-drug treatment, caspase-8 activation triggered downstream executioner caspase-3 and, to a lesser degree, caspase-7.
Conclusion: In our experimental models, characterized by different biomolecular profiles representing the different biology of human breast cancers, the schedule Dox-->Pacl-->48-h washout-->5-FU was highly active and schedule-dependent and has recently been used to plan a phase I/II clinical protocol.
Figures
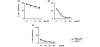



References
-
- Weiss RB, Woolf SH, Demakos E, Holland JF, Berry DA, Falkson G, Cirrincione CT, Robbins A, Bothun S, Henderson IC, et al. Natural history of more than 20 years of node-positive primary breast carcinoma treated with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy: a study by the Cancer and Leukemia Group B. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1825–1835. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.09.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Broker LE, Huisman C, Span SW, Rodriguez JA, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G. Cathepsin B mediates caspase-independent cell death induced by microtubule stabilizing agents in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:27–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

