Chromosomal copy number changes in patients with non-syndromic X linked mental retardation detected by array CGH
- PMID: 16169931
- PMCID: PMC2563232
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg.2005.036178
Chromosomal copy number changes in patients with non-syndromic X linked mental retardation detected by array CGH
Erratum in
- J Med Genet. 2008 Dec;45(12):832
Abstract
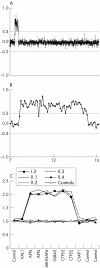
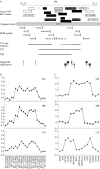
Several studies have shown that array based comparative genomic hybridisation (CGH) is a powerful tool for the detection of copy number changes in the genome of individuals with a congenital disorder. In this study, 40 patients with non-specific X linked mental retardation were analysed with full coverage, X chromosomal, bacterial artificial chromosome arrays. Copy number changes were validated by multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification as a fast method to detect duplications and deletions in patient and control DNA. This approach has the capacity to detect copy number changes as small as 100 kb. We identified three causative duplications: one family with a 7 Mb duplication in Xp22.2 and two families with a 500 kb duplication in Xq28 encompassing the MECP2 gene. In addition, we detected four regions with copy number changes that were frequently identified in our group of patients and therefore most likely represent genomic polymorphisms. These results confirm the power of array CGH as a diagnostic tool, but also emphasise the necessity to perform proper validation experiments by an independent technique.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: there are no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
X chromosome array-CGH for the identification of novel X-linked mental retardation genes.Eur J Med Genet. 2005 Jul-Sep;48(3):263-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2005.04.008. Eur J Med Genet. 2005. PMID: 16179222
-
Structural variation in Xq28: MECP2 duplications in 1% of patients with unexplained XLMR and in 2% of male patients with severe encephalopathy.Eur J Hum Genet. 2009 Apr;17(4):444-53. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2008.208. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Eur J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 18985075 Free PMC article.
-
Copy-number variations on the X chromosome in Japanese patients with mental retardation detected by array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis.J Hum Genet. 2010 Sep;55(9):590-9. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2010.74. Epub 2010 Jul 8. J Hum Genet. 2010. PMID: 20613765
-
Characterisation of hairy cell leukaemia by tiling resolution array-based comparative genome hybridisation: a series of 13 cases and review of the literature.Eur J Haematol. 2010 Jan 1;84(1):17-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.2009.01334.x. Eur J Haematol. 2010. PMID: 19682064 Review.
-
Genomic microarrays in mental retardation: a practical workflow for diagnostic applications.Hum Mutat. 2009 Mar;30(3):283-92. doi: 10.1002/humu.20883. Hum Mutat. 2009. PMID: 19085936 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-autonomous alterations in dendritic arbor morphology and connectivity induced by overexpression of MeCP2 in Xenopus central neurons in vivo.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033153. Epub 2012 Mar 9. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22427975 Free PMC article.
-
Distal Xq duplication and functional Xq disomy.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009 Feb 20;4:4. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-4-4. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009. PMID: 19232094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new normalizing algorithm for BAC CGH arrays with quality control metrics.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:860732. doi: 10.1155/2011/860732. Epub 2011 Feb 21. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21403910 Free PMC article.
-
High frequency of nonrecurrent MECP2 duplications among Brazilian males with mental retardation.J Mol Neurosci. 2010 May;41(1):105-9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-009-9296-2. Epub 2009 Oct 6. J Mol Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 19806472
-
Autism and other neuropsychiatric symptoms are prevalent in individuals with MeCP2 duplication syndrome.Ann Neurol. 2009 Dec;66(6):771-82. doi: 10.1002/ana.21715. Ann Neurol. 2009. PMID: 20035514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Association on Mental Retardation Mental retardation: definition, classification, and systems of supports. 10th ed. Washington DC: American Association on Mental Retardation, 2002;9
-
- Stevenson R E, Schwartz C E, Schroer R J.X‐linked mental retardation. New York: Oxford University Press, 2000
-
- Mandel J L, Chelly J. Monogenic X‐linked mental retardation: is it as frequent as currently estimated? The paradox of the ARX (Aristaless X) mutations. Eur J Hum Genet 200412689–693. - PubMed
-
- Ropers H H, Hamel B C. X‐linked mental retardation. Nat Rev Genet 2005646–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous