Importance of the GP dipeptide of the antiporter motif and other membrane-embedded proline and glycine residues in tetracycline efflux protein Tet(L)
- PMID: 16171405
- PMCID: PMC2515593
- DOI: 10.1021/bi050762c
Importance of the GP dipeptide of the antiporter motif and other membrane-embedded proline and glycine residues in tetracycline efflux protein Tet(L)
Abstract
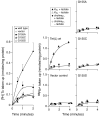
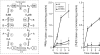
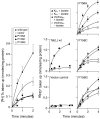
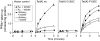
Proline and glycine residues are well represented among functionally important residues in hydrophobic domains of membrane transport proteins, and several critical roles have been suggested for them. Here, the effects of mutational changes in membrane-embedded proline and glycine residues of Tet(L) were examined, with a focus on the conserved GP(155,156) dipeptide of motif C, a putative "antiporter motif". Mutation of Gly155 to cysteine resulted in a mutant Tet(L) that bound its tetracycline-divalent metal (Tc-Me2+) substrate but did not catalyze efflux or exchange of Tc-Me2+ or catalyze uptake or exchange of Rb+ which was used to monitor the coupling ion. These results support suggestions that this region is involved in the conformational changes required for translocation. Mutations in Pro156 resulted in reduction (P156G) or loss (P156A or P156C) of Tc-Me2+ efflux capacity. All three Pro156 mutants exhibited a K+ leak (monitored by 86Rb+ fluxes) that was not observed in wild-type Tet(L). A similar leak was observed in a mutant in a membrane-embedded proline residue elsewhere in the Tet(L) protein (P175C) as well as in a P156C mutant of related antiporter Tet(K). These findings are consistent with roles proposed for membrane-embedded prolines in tight helix packing. Patterns of Tc resistance conferred by additional Tet(L) mutants indicate important roles for another GP dipeptide in transmembrane segment (TMS) X as well as for membrane-embedded glycine residues in TMS XIII.
Figures



References
-
- Landolt-Marticorena C, Williams KA, Deber CM, Reithmeier RA. Non-random distribution of amino acids in the transmembrane segments of human type I single span membrane proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1993;229:602–608. - PubMed
-
- Cordes FS, Bright JN, Sansom MS. Proline-induced distortions of transmembrane helices. J. Mol. Biol. 2002;323:951–960. - PubMed
-
- O'Neil KT, DeGrado WF. A thermodynamic scale for the helix-forming tendencies of the commonly occurring amino acids. Science. 1990;250:646–651. - PubMed
-
- Williams KA, Deber CM. Proline residues in transmembrane helices: structural or dynamic role? Biochemistry. 1991;30:8919–8923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

