Cell adhesion molecules regulate Ca2+-mediated steering of growth cones via cyclic AMP and ryanodine receptor type 3
- PMID: 16172206
- PMCID: PMC2171540
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200503157
Cell adhesion molecules regulate Ca2+-mediated steering of growth cones via cyclic AMP and ryanodine receptor type 3
Abstract
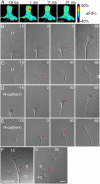
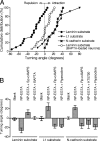
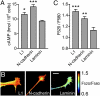
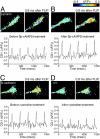
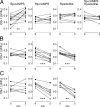
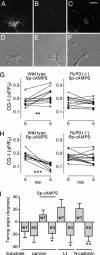
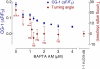
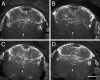
Axonal growth cones migrate along the correct paths during development, not only directed by guidance cues but also contacted by local environment via cell adhesion molecules (CAMs). Asymmetric Ca2+ elevations in the growth cone cytosol induce both attractive and repulsive turning in response to the guidance cues (Zheng, J.Q. 2000. Nature. 403:89-93; Henley, J.R., K.H. Huang, D. Wang, and M.M. Poo. 2004. Neuron. 44:909-916). Here, we show that CAMs regulate the activity of ryanodine receptor type 3 (RyR3) via cAMP and protein kinase A in dorsal root ganglion neurons. The activated RyR3 mediates Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release (CICR) into the cytosol, leading to attractive turning of the growth cone. In contrast, the growth cone exhibits repulsion when Ca2+ signals are not accompanied by RyR3-mediated CICR. We also propose that the source of Ca2+ influx, rather than its amplitude or the baseline Ca2+ level, is the primary determinant of the turning direction. In this way, axon-guiding and CAM-derived signals are integrated by RyR3, which serves as a key regulator of growth cone navigation.
Figures
References
-
- Adams, S.R., A.T. Harootunian, Y.J. Buechler, S.S. Taylor, and R.Y. Tsien. 1991. Fluorescence ratio imaging of cyclic AMP in single cells. Nature. 349:694–697. - PubMed
-
- Augustine, G.J., F. Santamaria, and K. Tanaka. 2003. Local calcium signaling in neurons. Neuron. 40:331–346. - PubMed
-
- Bouchard, R., R. Pattarini, and J.D. Geiger. 2003. Presence and functional significance of presynaptic ryanodine receptors. Prog. Neurobiol. 69:391–418. - PubMed
-
- Brummendorf, T., and F.G. Rathjen. 1994. Cell adhesion molecules. 1: immunoglobulin superfamily. Protein Profile. 1:951–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

