Divergent responses of chondrocytes and endothelial cells to shear stress: cross-talk among COX-2, the phase 2 response, and apoptosis
- PMID: 16172382
- PMCID: PMC1236575
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506620102
Divergent responses of chondrocytes and endothelial cells to shear stress: cross-talk among COX-2, the phase 2 response, and apoptosis
Abstract
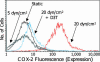
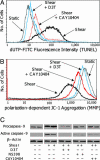
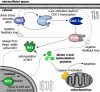
Fluid shear exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects on endothelial cells by inducing the coordinated expression of phase 2 detoxifying and antioxidant genes. In contrast, high shear is pro-apoptotic in chondrocytes and promotes matrix degradation and cartilage destruction. We have analyzed the mechanisms regulating shear-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis by cDNA microarray technology and bioinformatics. We demonstrate that shear-induced cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 suppresses phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K) activity, which represses antioxidant response element (ARE)/NF-E2 related factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated transcriptional response in human chondrocytes. The resultant decrease in antioxidant capacity of sheared chondrocytes contributes to their apoptosis. Phase 2 inducers, and to a lesser extent COX-2-selective inhibitors, negate the shear-mediated suppression of ARE-driven phase 2 activity and apoptosis. The abrogation of shear-induced COX-2 expression by PI3-K activity and/or stimulation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway suggests the existence of PI3-K/Nrf2/ARE negative feedback loops that potentially interfere with c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 activity upstream of COX-2. Reconstructing the signaling network regulating shear-induced chondrocyte apoptosis may provide insights to optimize conditions for culturing artificial cartilage in bioreactors and for developing therapeutic strategies for arthritic disorders.
Figures
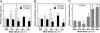




References
-
- Chen, X. L., Varner, S. E., Rao, A. S., Grey, J. Y., Thomas, S., Cook, C. K., Wasserman, M. A., Medford, R. M., Jaiswal, A. K. & Kunsch, C. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 703-711. - PubMed
-
- Hosoya, T., Maruyama, A., Kang, M. I., Kawatani, Y., Shibata, T., Uchida, K., Itoh, K. & Yamamoto, M. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 27244-27250. - PubMed
-
- Dimmeler, S., Haendeler, J., Rippmann, V., Nehls, M. & Zeiher, A. M. (1996) FEBS Lett. 399, 71-74. - PubMed
-
- Jang, J. H. & Surh, Y. J. (2003) Biochem. Pharmacol. 66, 1371-1379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

