Bifurcated converging pathways for high Ca2+- and TGFbeta-induced inhibition of growth of normal human keratinocytes
- PMID: 16172401
- PMCID: PMC1216828
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0500630102
Bifurcated converging pathways for high Ca2+- and TGFbeta-induced inhibition of growth of normal human keratinocytes
Abstract
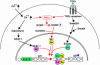
Growth suppression of normal human keratinocytes by high Ca2+ or TGFbeta was shown to be mediated by p21WAF1/CIP1 and Sp1 [Pardali, K., et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 29244-29256; Santini, M. P., Talora, C., Seki, T., Bolgan, L. & Dotto, G. P. (2001) Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9575-9580; Al-Daraji, W. I., Grant, K. R., Ryan, K., Saxton, A., & Reynolds, N. J. (2002) J. Invest. Dermatol. 118, 779-788]. We previously demonstrated that S100C/A11 is a key mediator for growth inhibition of normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHK) triggered by high Ca2+ or TGFbeta [Sakaguchi, M., et al. (2003) J. Cell Biol. 163, 825-835; Sakaguchi, M., et al. (2004) 164, 979-984]. On exposure of NHK cells to either agent, S100C/A11 is transferred to nuclei, where it induces p21WAF1/CIP1 through activation of Sp1/Sp3. In the present study, we found that high Ca2+ activated NFAT1 through calcineurin-dependent dephosphorylation. In growing NHK cells, Krueppel-like factor (KLF)16, a member of the Sp/KLF family, bound to the p21WAF1/CIP1 promoter and, thereby, inhibited the transcription of p21(WAF1/CIP1). Sp1 complexed with NFAT1 in high Ca2+-treated cells or with Smad3 in TGFbeta1-treated cells, but not Sp1 alone, replaced KLF16 from the p21WAF1/CIP1 promoter and transcriptionally activated the p21WAF1/CIP1 gene. Thus, high Ca2+ and TGFbeta1 have a common S100C/A11-mediated pathway in addition to a unique pathway (NFAT1-mediated pathway for high Ca2+ and Smad-mediated pathway for TGFbeta1) for exhibiting a growth inhibitory effect on NHK cells, and both pathways were shown to be indispensable for growth inhibition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PKCalpha mediates TGFbeta-induced growth inhibition of human keratinocytes via phosphorylation of S100C/A11.J Cell Biol. 2004 Mar 29;164(7):979-84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200312041. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15051732 Free PMC article.
-
S100C/A11 is a key mediator of Ca(2+)-induced growth inhibition of human epidermal keratinocytes.J Cell Biol. 2003 Nov 24;163(4):825-35. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200304017. Epub 2003 Nov 17. J Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14623863 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of H2O2-mediated ERK activation with Smad pathway in TGF-beta1 induction of p21WAF1/Cip1.Cell Signal. 2006 Feb;18(2):236-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.04.008. Epub 2005 Jun 24. Cell Signal. 2006. PMID: 15979845
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
TGFbeta regulated gene expression by Smads and Sp1/KLF-like transcription factors in cancer.Anticancer Res. 2008 May-Jun;28(3A):1531-9. Anticancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18630508 Review.
Cited by
-
High expression of S100A11 in pancreatic adenocarcinoma is an unfavorable prognostic marker.Med Oncol. 2012 Sep;29(3):1886-91. doi: 10.1007/s12032-011-0058-y. Epub 2011 Sep 13. Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21912994
-
Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals Spatial and Temporal Turnover of Keratinocyte Differentiation Regulators.Front Genet. 2019 Sep 3;10:775. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00775. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31552090 Free PMC article.
-
Dramatic increase in expression of a transgene by insertion of promoters downstream of the cargo gene.Mol Biotechnol. 2014 Jul;56(7):621-30. doi: 10.1007/s12033-014-9738-0. Mol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24526517 Free PMC article.
-
Krüppel-like factors: three fingers in control.Hum Genomics. 2010 Apr;4(4):263-70. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-4-4-263. Hum Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20511139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Palmitic Acid Methyl Ester Induces G2/M Arrest in Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells via the p53/p21 Pathway.Stem Cells Int. 2019 Dec 1;2019:7606238. doi: 10.1155/2019/7606238. eCollection 2019. Stem Cells Int. 2019. PMID: 31885624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rheinwald, J. G. & Green, H. (1975) Cell 6, 331–343. - PubMed
-
- Boyce, S. T. & Ham, R. G. (1983) J. Invest. Dermatol. 81, Suppl. 1, S33–S40. - PubMed
-
- Sharpe, G. R., Gillespie, J. I. & Greenwell, J. R. (1989) FEBS Lett. 254, 25–28. - PubMed
-
- Shipley, G. D., Pittelkow, M. R., Wille, J. J., Jr., Scott, R. E. & Moses, H. L. (1986) Cancer Res. 46, 2068–2071. - PubMed
-
- Moses, H. L., Yang, E. Y. & Pietenpol, J. A. (1991) Ciba Found. Symp. 157, 66–74, discussion 75–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

