Low-renin hypertension with relative aldosterone excess is associated with impaired NO-mediated vasodilation
- PMID: 16172426
- PMCID: PMC2737344
- DOI: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000184231.84465.62
Low-renin hypertension with relative aldosterone excess is associated with impaired NO-mediated vasodilation
Erratum in
- Hypertension. 2005 Dec;46(6):e26
Abstract
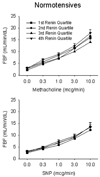
Recent studies suggest that hypertension associated with low renin status and hyperaldosteronism is associated with increased risk for end-organ damage and cardiovascular events compared with other forms of hypertension. Additionally, experimental studies have demonstrated impaired nitric oxide-mediated bioactivity in these states. To investigate the relation between renin/aldosterone status and resistance vessel function, we examined plasma renin activity, serum aldosterone level, and forearm blood flow responses to the endothelium-dependent vasodilator methacholine and the endothelium-independent vasodilators sodium nitroprusside and verapamil using venous occlusion plethysmography in 130 volunteers (43 hypertensive, 87 normotensive). Low renin status was associated with impaired responses to methacholine and nitroprusside in patients with hypertension. Peak methacholine response was 8.7+/-5.6 mL/min per dL in the lowest renin quartile (0.1 to 0.3 ng/mL per hour) versus 14.3+/-7.3 mL/min per dL in the highest 3 renin quartiles combined (0.4 to 4.6 ng/mL per hour; P<0.001). Peak nitroprusside response was 5.6+/-2.3 mL/min per dL in the lowest renin quartile versus 13.3+/-4.1 mL/min per dL in the highest 3 renin quartiles combined (P<0.001). Blood pressure and other clinical characteristics were similar in all 4 quartiles. Vasodilator responses to verapamil did not relate to renin activity. Methacholine and nitroprusside responses did not relate to renin status in normotensive controls (P=0.34). Importantly, hypertensive patients with a high aldosterone/renin ratio also had impaired responses to methacholine. This study demonstrates that low-renin hypertension is associated with marked impairment of nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation of resistance vessels in the forearm vasculature of humans. This impairment could contribute to adverse outcomes in patients with low-renin hypertension and relative aldosterone excess.
Figures



Comment in
-
Relative aldosterone excess: relative to what?Hypertension. 2005 Oct;46(4):643-4. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000184227.75221.6e. Epub 2005 Sep 19. Hypertension. 2005. PMID: 16172414 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Impaired endothelium-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation in hypertensive subjects with hyperaldosteronism.Circulation. 2004 Jun 15;109(23):2857-61. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000129307.26791.8E. Epub 2004 Jun 1. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15173035
-
Impaired nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Mar 1;27(3):567-74. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(95)00522-6. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996. PMID: 8606266
-
Dietary sodium intake modulates vasodilation mediated by nitroprusside but not by methacholine in the human forearm.Hypertension. 1995 Jun;25(6):1220-3. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.25.6.1220. Hypertension. 1995. PMID: 7768565
-
Vasodilation in black Americans: attenuated nitric oxide-mediated responses.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Oct;62(4):436-43. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9236(97)90122-3. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1997. PMID: 9357395
-
Effect of insulin on acetylcholine-induced vasodilation in normotensive subjects and patients with essential hypertension.Circulation. 1995 Nov 15;92(10):2911-8. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.92.10.2911. Circulation. 1995. PMID: 7586259
Cited by
-
Quantification of systemic renin-angiotensin system peptides of hypertensive black and white African men established from the RAS-Fingerprint®.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2016 Oct 12;17(4):1470320316669880. doi: 10.1177/1470320316669880. Print 2016 Oct. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2016. PMID: 27737932 Free PMC article.
-
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system gender differences in an Afro-Caribbean population.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015 Sep;16(3):539-46. doi: 10.1177/1470320314523659. Epub 2014 Feb 14. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015. PMID: 24532825 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of aldosterone-producing adenoma on endothelial function and Rho-associated kinase activity in patients with primary aldosteronism.Hypertension. 2015 Apr;65(4):841-8. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.05001. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25624340 Free PMC article.
-
Aldosterone affects blood flow and vascular tone regulated by endothelium-derived NO: therapeutic implications.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;168(3):519-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02194.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23190073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AT1 receptors prevent salt-induced vascular dysfunction in isolated middle cerebral arteries of 2 kidney-1 clip hypertensive rats.Am J Hypertens. 2013 Dec;26(12):1398-404. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpt129. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Am J Hypertens. 2013. PMID: 23934707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brunner HR, Laragh JH, Baer L, Newton MA, Goodwin FT, Krakoff LR, Bard RH, Buhler FR. Essential hypertension: renin and aldosterone, heart attack and stroke. N Engl J Med. 1972;286:441–449. - PubMed
-
- Weinberger MH, Miller JZ, Luft FC, Grim CE, Fineberg NS. Definitions and characteristics of sodium sensitivity and blood pressure resistance. Hypertension. 1986;8:II127–II134. - PubMed
-
- Campese VM. Salt sensitivity in hypertension. Renal and cardiovascular implications. Hypertension. 1994;23:531–550. - PubMed
-
- Warnock DG. Low-renin and nonmodulating essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1999;34:395–397. - PubMed
-
- Conn JW, Cohen EL, Rovner DR, Nesbit RM. Normokalemic primary aldosteronism. A detectable cause of curable “essential” hypertension. J Am Med Assoc. 1965;193:200–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

