Serum glial fibrillary acidic protein as a biomarker for intracerebral haemorrhage in patients with acute stroke
- PMID: 16174653
- PMCID: PMC2077601
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.2005.074823
Serum glial fibrillary acidic protein as a biomarker for intracerebral haemorrhage in patients with acute stroke
Abstract
Background: Biomarkers of stroke are an evolving field of clinical research. A serum marker which can differentiate between haemorrhagic and ischaemic stroke in the very early phase would help to optimise acute stroke management.
Objective: To examine whether serum glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) identifies intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) in acute stroke patients.
Methods: A pilot study assessing 135 stroke patients admitted within six hours after symptom onset. Diagnosis of ICH (n = 42) or ischaemic stroke (n = 93) was based on brain imaging. GFAP was determined from venous blood samples obtained immediately after admission, using a research immunoassay.
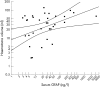
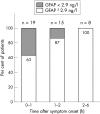
Results: GFAP was detectable in the serum of 39 patients (34 of 42 (81%) with ICH, and five of 93 (5%) with ischaemic stroke). Serum GFAP was substantially raised in patients with ICH (median 11 ng/l, range 0 to 3096 ng/l) compared with patients with ischaemic stroke (median 0 ng/l, range 0 to 14 ng/l, p<0.001). Using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, a cut off point of 2.9 ng/l provided a sensitivity of 0.79 and a specificity of 0.98 for the identification of ICH in acute stroke (positive predictive value 0.94, negative predictive value 0.91; p<0.001).
Conclusions: Serum GFAP can reliably detect ICH in the acute phase of stroke. Further evaluation of the usefulness of GFAP as an early diagnostic marker of ICH is now required, with the aim of optimising cause specific emergency management.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Christian Foerch and Matthias Sitzer are designated as inventors in the European patent application cited below. Ingo Curdt was employed as a scientific trainee by Roche Centralised Diagnostics, 82377 Penzberg, Germany; he is also designated as an inventor in the European patent application cited below. Title of pending patent: “Use of GFAP for identification of intracerebral haemorrhage” (patent application number: 03021571.9; date of filing: 24 September 2003. Bernard Yan, Florian Dvorak, Marcella Hermans, Joachim Berkefeld, Andreas Raabe, Tobias Neumann Haefelin, and Helmuth Steinmetz declare they have no competing interests.
References
-
- Sudlow C L, Warlow C P. Comparable studies of the incidence of stroke and its pathological types: results from an international collaboration. International Stroke Incidence Collaboration. Stroke 199728491–499. - PubMed
-
- Juvela S, Hillbom M, Palomaki H. Risk factors for spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 1995261558–1564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous