Neuronal sorting protein-related receptor sorLA/LR11 regulates processing of the amyloid precursor protein
- PMID: 16174740
- PMCID: PMC1224625
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0503689102
Neuronal sorting protein-related receptor sorLA/LR11 regulates processing of the amyloid precursor protein
Abstract
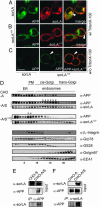
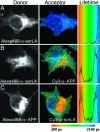
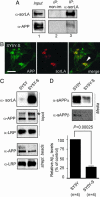
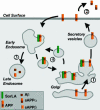
sorLA (Sorting protein-related receptor) is a type-1 membrane protein of unknown function that is expressed in neurons. Its homology to sorting receptors that shuttle between the plasma membrane, endosomes, and the Golgi suggests a related function in neuronal trafficking processes. Because expression of sorLA is reduced in the brain of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), we tested involvement of this receptor in intracellular transport and processing of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) to the amyloid beta-peptide (Abeta), the principal component of senile plaques. We demonstrate that sorLA interacts with APP in vitro and in living cells and that both proteins colocalize in endosomal and Golgi compartments. Overexpression of sorLA in neurons causes redistribution of APP to the Golgi and decreased processing to Abeta, whereas ablation of sorLA expression in knockout mice results in increased levels of Abeta in the brain similar to the situation in AD patients. Thus, sorLA acts as a sorting receptor that protects APP from processing into Abeta and thereby reduces the burden of amyloidogenic peptide formation. Consequently, reduced receptor expression in the human brain may increase Abeta production and plaque formation and promote spontaneous AD.
Figures


References
-
- Hermans-Borgmeyer, I., Hampe, W., Schinke, B., Methner, A., Nykjaer, A., Susens, U., Fenger, U., Herbarth, B. & Schaller, H. C. (1998) Mech. Dev. 70, 65-76. - PubMed
-
- Motoi, Y., Aizawa, T., Haga, S., Nakamura, S., Namba, Y. & Ikeda, K. (1999) Brain Res. 833, 209-215. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen, L., Madsen, P., Moestrup, S. K., Lund, A. H., Tommerup, N., Nykjaer, A., Sottrup-Jensen, L., Gliemann, J. & Petersen, C. M. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271, 31379-31383. - PubMed
-
- Yamazaki, H., Bujo, H., Kusunoki, J., Seimiya, K., Kanaki, T., Morisaki, N., Schneider, W. J. & Saito, Y. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271, 24761-24768. - PubMed
-
- Marcusson, E. G., Horazdovsky, B. F., Cereghino, J. L., Gharakhanian, E. & Emr, S. D. (1994) Cell 77, 579-586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

