Distinct functional units of the Golgi complex in Drosophila cells
- PMID: 16174741
- PMCID: PMC1224666
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506681102
Distinct functional units of the Golgi complex in Drosophila cells
Abstract
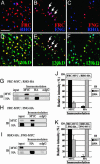
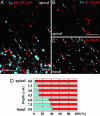
A striking variety of glycosylation occur in the Golgi complex in a protein-specific manner, but how this diversity and specificity are achieved remains unclear. Here we show that stacked fragments (units) of the Golgi complex dispersed in Drosophila imaginal disk cells are functionally diverse. The UDP-sugar transporter FRINGE-CONNECTION (FRC) is localized to a subset of the Golgi units distinct from those harboring SULFATELESS (SFL), which modifies glucosaminoglycans (GAGs), and from those harboring the protease RHOMBOID (RHO), which processes the glycoprotein SPITZ (SPI). Whereas the glycosylation and function of NOTCH are affected in imaginal disks of frc mutants, those of SPI and of GAG core proteins are not, even though FRC transports a broad range of glycosylation substrates, suggesting that Golgi units containing FRC and those containing SFL or RHO are functionally separable. Distinct Golgi units containing FRC and RHO in embryos could also be separated biochemically by immunoisolation techniques. We also show that Tn-antigen glycan is localized only in a subset of the Golgi units distributed basally in a polarized cell. We propose that the different localizations among distinct Golgi units of molecules involved in glycosylation underlie the diversity of glycan modification.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sugar-free frosting, a homolog of SAD kinase, drives neural-specific glycan expression in the Drosophila embryo.Development. 2011 Feb;138(3):553-63. doi: 10.1242/dev.055376. Development. 2011. PMID: 21205799 Free PMC article.
-
Two pathways for importing GDP-fucose into the endoplasmic reticulum lumen function redundantly in the O-fucosylation of Notch in Drosophila.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 5;285(6):4122-4129. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.016964. Epub 2009 Nov 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19948734 Free PMC article.
-
Cisterna-specific localization of glycosylation-related proteins to the Golgi apparatus.Cell Struct Funct. 2012;37(1):55-63. doi: 10.1247/csf.11037. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Cell Struct Funct. 2012. PMID: 22251795
-
[Regulation of glycosylation in Golgi units].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2008 Sep;53(12 Suppl):1475-9. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2008. PMID: 21089351 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
What can yeast tell us about N-linked glycosylation in the Golgi apparatus?FEBS Lett. 2001 Jun 8;498(2-3):223-7. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02488-7. FEBS Lett. 2001. PMID: 11412862 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of genes required for neural-specific glycosylation using functional genomics.PLoS Genet. 2010 Dec 23;6(12):e1001254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001254. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 21203496 Free PMC article.
-
Sugar-free frosting, a homolog of SAD kinase, drives neural-specific glycan expression in the Drosophila embryo.Development. 2011 Feb;138(3):553-63. doi: 10.1242/dev.055376. Development. 2011. PMID: 21205799 Free PMC article.
-
Segregation of the membrane cargoes, BACE1 and amyloid precursor protein (APP) throughout the Golgi apparatus.Traffic. 2022 Mar;23(3):158-173. doi: 10.1111/tra.12831. Epub 2022 Feb 13. Traffic. 2022. PMID: 35076977 Free PMC article.
-
Wolbachia bacteria reside in host Golgi-related vesicles whose position is regulated by polarity proteins.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022703. Epub 2011 Jul 28. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21829485 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Sec16 mediates the biogenesis of tER sites upstream of Sar1 through an arginine-rich motif.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Oct;19(10):4352-65. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-03-0246. Epub 2008 Jul 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18614796 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

