Linkage and association studies identify a novel locus for Alzheimer disease at 7q36 in a Dutch population-based sample
- PMID: 16175510
- PMCID: PMC1275613
- DOI: 10.1086/491749
Linkage and association studies identify a novel locus for Alzheimer disease at 7q36 in a Dutch population-based sample
Abstract
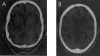
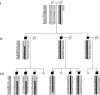
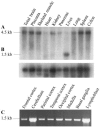
We obtained conclusive linkage of Alzheimer disease (AD) with a candidate region of 19.7 cM at 7q36 in an extended multiplex family, family 1270, ascertained in a population-based study of early-onset AD in the northern Netherlands. Single-nucleotide polymorphism and haplotype association analyses of a Dutch patient-control sample further supported the linkage at 7q36. In addition, we identified a shared haplotype at 7q36 between family 1270 and three of six multiplex AD-affected families from the same geographical region, which is indicative of a founder effect and defines a priority region of 9.3 cM. Mutation analysis of coding exons of 29 candidate genes identified one linked synonymous mutation, g.38030G-->C in exon 10, that affected codon 626 of the PAX transactivation domain interacting protein gene (PAXIP1). It remains to be determined whether PAXIP1 has a functional role in the expression of AD in family 1270 or whether another mutation at this locus explains the observed linkage and sharing. Together, our linkage data from the informative family 1270 and the association data in the population-based early-onset AD patient-control sample strongly support the identification of a novel AD locus at 7q36 and re-emphasize the genetic heterogeneity of AD.
Figures





Comment in
-
Lack of evidence supporting a role for DPP6 sequence variants in Alzheimer's disease in the European American population.Acta Neuropathol. 2021 Apr;141(4):623-624. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02271-w. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Acta Neuropathol. 2021. PMID: 33591372 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply: Lack of evidence supporting a role for DPP6 sequence variants in Alzheimer's disease in the European American population.Acta Neuropathol. 2021 Apr;141(4):625-626. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02277-4. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Acta Neuropathol. 2021. PMID: 33591373 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A genomewide screen for late-onset Alzheimer disease in a genetically isolated Dutch population.Am J Hum Genet. 2007 Jul;81(1):17-31. doi: 10.1086/518720. Epub 2007 May 29. Am J Hum Genet. 2007. PMID: 17564960 Free PMC article.
-
Dense-map genome scan for dyslexia supports loci at 4q13, 16p12, 17q22; suggests novel locus at 7q36.Genes Brain Behav. 2013 Feb;12(1):56-69. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12003. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Genes Brain Behav. 2013. PMID: 23190410
-
A population-based study of familial Alzheimer disease: linkage to chromosomes 14, 19, and 21.Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Oct;55(4):714-27. Am J Hum Genet. 1994. PMID: 7942850 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage and association study of late-onset Alzheimer disease families linked to 9p21.3.Ann Hum Genet. 2008 Nov;72(Pt 6):725-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2008.00474.x. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Ann Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18761660 Free PMC article.
-
Ascertainment of informative Alzheimer disease families from the IMAGE Project registry for genetic linkage analysis studies.Can J Neurol Sci. 1989 Nov;16(4 Suppl):468-72. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100029784. Can J Neurol Sci. 1989. PMID: 2680006 Review.
Cited by
-
Endophenotypes in normal brain morphology and Alzheimer's disease: a review.Neuroscience. 2009 Nov 24;164(1):174-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.04.006. Epub 2009 Apr 9. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19362127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for three loci modifying age-at-onset of Alzheimer's disease in early-onset PSEN2 families.Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010 Jul;153B(5):1031-41. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.31072. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010. PMID: 20333730 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of pedigree data in populations with multiple ancestries: Strategies for dealing with admixture in Caribbean Hispanic families from the ADSP.Genet Epidemiol. 2018 Sep;42(6):500-515. doi: 10.1002/gepi.22133. Epub 2018 Jun 3. Genet Epidemiol. 2018. PMID: 29862559 Free PMC article.
-
Age-at-onset linkage analysis in Caribbean Hispanics with familial late-onset Alzheimer's disease.Neurogenetics. 2008 Feb;9(1):51-60. doi: 10.1007/s10048-007-0103-3. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Neurogenetics. 2008. PMID: 17940814 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of Alzheimer's disease: a centennial review.Neurol Clin. 2007 Aug;25(3):611-67, v. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2007.03.009. Neurol Clin. 2007. PMID: 17659183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Web Resources
-
- Arlequin, http://lgb.unige.ch/arlequin/ (for estimation of haplotype frequencies)
-
- Alzheimer Disease & Frontotemporal Dementia Mutation Database, http://www.molgen.ua.ac.be/ADMutations/
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for the Marshfield Medical Research Foundation and marker position and extra markers in region of interest)
-
- Cooperative Human Linkage Center, http://gai.nci.nih.gov/CHLC/ (for extra marker in region of interest)
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for PAXIP1 [accession numbers AC093726.3 and NM_007349.6], ABCF2 [accession number AC021097.5], GALNT11 [accession number AC074257.5], DPP6 [accession number AC006019.2], and EN2 [accession number AC008060.5])
References
-
- Ashley-Koch AE, Shao Y, Rimmler JB, Gaskell PC, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Jackson CE, Scott WK, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (2005) An autosomal genomic screen for dementia in an extended Amish family. Neurosci Lett 379:199–204 - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261:921–923 - PubMed
-
- Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C (1998) Presenilin mutations in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mutat 11:183–190 - PubMed
-
- Cruts M, van Duijn CM, Backhovens H, Van den BM, Wehnert A, Serneels S, Sherrington R, Hutton M, Hardy J, George-Hyslop PH, Hofman A, Van Broeckhoven C (1998) Estimation of the genetic contribution of presenilin-1 and -2 mutations in a population-based study of presenile Alzheimer disease. Hum Mol Genet 7:43–51 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

