Reciprocal role of cyclins and cyclin kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 on lymphocyte proliferation, allo-immune activation and inflammation
- PMID: 16176581
- PMCID: PMC1242230
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-6-22
Reciprocal role of cyclins and cyclin kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 on lymphocyte proliferation, allo-immune activation and inflammation
Abstract
Background: Immune activation that results due to the aberrant proliferation of lymphocytes leads to inflammation and graft rejection in organ transplant recipients. We hypothesize that the cell cycle control and inflammation are parallel events, inhibition of cellular proliferation by cyclin kinase inhibitor specifically p21 will limit inflammation and prevent allograft rejection.
Methods: We performed in vitro and in vivo studies using lymphocytes, and rat heart transplant model to understand the role of cyclins and p21 on mitogen and allo-induced lymphocyte activation and inflammation. Lymphocyte proliferation was studied by 3H-thymidine uptake assay and mRNA expression was studied RT-PCR.
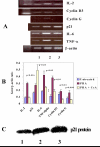
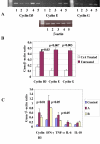
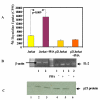
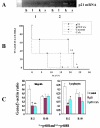
Results: Activation of allo- and mitogen stimulated lymphocytes resulted in increased expression of cyclins, IL-2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which was inhibited by cyclosporine. The over-expression of p21 prolonged graft survival in a completely mismatched rat heart transplant model resulted by inhibiting circulating and intra-graft expression of proinflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion: Cyclins play a significant role in transplant-induced immune activation and p21 over-expression has potential to inhibit T cell activation and inflammation. The results from this study will permit the design of alternate strategies by controlling cell cycle progression to achieve immunosuppression in transplantation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeted in vitro and in vivo gene transfer into T lymphocytes: potential of direct inhibition of allo-immune activation.BMC Immunol. 2006 Nov 10;7:26. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-7-26. BMC Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17096842 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of Isatis tinctoria L. and tacrolimus in the prevention of acute heart rejection in mice.Transpl Immunol. 2009 Dec;22(1-2):5-11. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2009.09.004. Epub 2009 Sep 18. Transpl Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19766187
-
In vitro and in vivo transfection of p21 gene enhances cyclosporin A-mediated inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation.J Immunol. 2000 Aug 15;165(4):1882-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.4.1882. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10925268
-
Eicosanoids and renal allograft rejection.Nephron. 1995;70(2):151-4. doi: 10.1159/000188577. Nephron. 1995. PMID: 7566297 Review.
-
Cytokines and organ transplantation. A review.Nucl Med Biol. 1994 Apr;21(3):545-55. doi: 10.1016/0969-8051(94)90076-0. Nucl Med Biol. 1994. PMID: 9234312 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain injury expands the numbers of neural stem cells and progenitors in the SVZ by enhancing their responsiveness to EGF.ASN Neuro. 2009 May 20;1(2):e00009. doi: 10.1042/AN20090002. ASN Neuro. 2009. PMID: 19570028 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of CDKN1A/p21 in HIV-1 controllers is correlated with upregulation of ZC3H12A/MCPIP1.Retrovirology. 2020 Jul 2;17(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12977-020-00522-4. Retrovirology. 2020. PMID: 32615986 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoengineered MXene nanosystem for mitigation of alloantigen presentation and prevention of transplant vasculopathy.Nano Today. 2023 Feb;48:None. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2022.101706. Nano Today. 2023. PMID: 37187503 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted in vitro and in vivo gene transfer into T lymphocytes: potential of direct inhibition of allo-immune activation.BMC Immunol. 2006 Nov 10;7:26. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-7-26. BMC Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17096842 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced susceptibility of cyclin kinase inhibitor p21 knockout mice to high fat diet induced atherosclerosis.J Biomed Sci. 2009 Jul 15;16(1):66. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-16-66. J Biomed Sci. 2009. PMID: 19604372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khanna A, Cairns V, Becker CG, Hosenpud JD. Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) mimics and anti-TGF-β antibody abrogates the in-vivo effects of Cyclosporine: demonstration of a direct role of TGF-β in immunosuppression and nephrotoxicity of CsA. Transplantation. 1999;67:882–882. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199903270-00016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

