The mitotic exit network Mob1p-Dbf2p kinase complex localizes to the nucleus and regulates passenger protein localization
- PMID: 16176976
- PMCID: PMC1289394
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-04-0337
The mitotic exit network Mob1p-Dbf2p kinase complex localizes to the nucleus and regulates passenger protein localization
Abstract
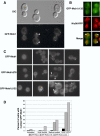
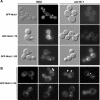
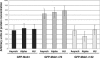
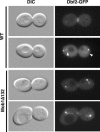
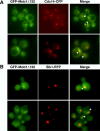
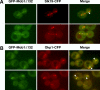
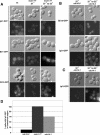
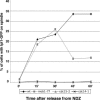
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitotic exit network (MEN) is a conserved signaling network that coordinates CDK inactivation, cytokinesis and G1 gene transcription. The MEN Cdc14p phosphatase is sequestered in the nucleolus and transiently released in early anaphase and telophase. Cdc14p mediates mitotic exit by dephosphorylating Cdk1p substrates and promoting Cdk1p inactivation. Cdc14p also regulates the localization of chromosomal passenger proteins, which redistribute from kinetochores to the mitotic spindle during anaphase. Here we present evidence that the MEN protein kinase complex Mob1p-Dbf2p localizes to mitotic nuclei and partially colocalizes with Cdc14p and kinetochore proteins. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments reveal that Mob1p, Dbf2p, and Cdc14p associate with centromere DNA and require the centromere binding protein Ndc10p for this association. We establish that Mob1p is essential for maintaining the localization of Aurora, INCENP, and Survivin chromosomal passenger proteins on anaphase spindles, whereas Cdc14p and the Mob1p-Dbf2p-activating kinase Cdc15p are required for establishing passenger protein localization on the spindle. Moreover, Mob1p, but not Cdc15p, is required for dissociating Aurora from the kinetochore region. These findings reveal kinetochores as sites for MEN signaling and implicate MEN in coordinating chromosome segregation and/or spindle integrity with mitotic exit and cytokinesis via regulation of chromosome passenger proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of the Bfa1p-Bub2p complex at spindle pole bodies by the cell cycle phosphatase Cdc14p.J Cell Biol. 2002 Apr 29;157(3):367-79. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200112085. Epub 2002 Apr 22. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11970961 Free PMC article.
-
Separase regulates INCENP-Aurora B anaphase spindle function through Cdc14.Science. 2003 Dec 19;302(5653):2120-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1091936. Epub 2003 Nov 6. Science. 2003. PMID: 14605209
-
The kinetochore protein Ndc10p is required for spindle stability and cytokinesis in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Apr 12;102(15):5408-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405925102. Epub 2005 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15809434 Free PMC article.
-
The role of centromere-binding factor 3 (CBF3) in spindle stability, cytokinesis, and kinetochore attachment.Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;83(6):696-702. doi: 10.1139/o05-161. Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16333320 Review.
-
Regulation of Mitotic Exit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1505:3-17. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6502-1_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27826852 Review.
Cited by
-
The NDR kinase DBF-2 is involved in regulation of mitosis, conidial development, and glycogen metabolism in Neurospora crassa.Eukaryot Cell. 2010 Apr;9(4):502-13. doi: 10.1128/EC.00230-09. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Eukaryot Cell. 2010. PMID: 19966031 Free PMC article.
-
MOB control: reviewing a conserved family of kinase regulators.Cell Signal. 2011 Sep;23(9):1433-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.04.007. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21539912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substrate analysis of the Pneumocystis carinii protein kinases PcCbk1 and PcSte20 using yeast proteome microarrays provides a novel method for Pneumocystis signalling biology.Yeast. 2011 Oct;28(10):707-19. doi: 10.1002/yea.1900. Epub 2011 Sep 8. Yeast. 2011. PMID: 21905091 Free PMC article.
-
A Bir1-Sli15 complex connects centromeres to microtubules and is required to sense kinetochore tension.Cell. 2006 Dec 15;127(6):1179-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.049. Cell. 2006. PMID: 17174893 Free PMC article.
-
Dbf2-Mob1 drives relocalization of protein phosphatase Cdc14 to the cytoplasm during exit from mitosis.J Cell Biol. 2009 Feb 23;184(4):527-39. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200812022. Epub 2009 Feb 16. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19221193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexandru, G., Uhlmann, F., Mechtler, K., Poupart, M. A., and Nasmyth, K. (2001). Phosphorylation of the cohesin subunit Scc1 by Polo/Cdc5 kinase regulates sister chromatid separation in yeast. Cell 105, 459–472. - PubMed
-
- Azzam, R., Chen, S. L., Shou, W., Mah, A. S., Alexandru, G., Nasmyth, K., Annan, R. S., Carr, S. A., and Deshaies, R. J. (2004). Phosphorylation by cyclin B-Cdk underlies release of mitotic exit activator Cdc14 from the nucleolus. Science 305, 516–519. - PubMed
-
- Bembenek, J., Kang, J., Kurischko, C., Li, B., Raab, J. R., Belanger, K. D., Luca, F. C., and Yu, H. (2005). Crm1-mediated nuclear export of Cdc14 is required for the completion of cytokinesis in budding yeast. Cell Cycle 4, 951–961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

