Amino acids mediate mTOR/raptor signaling through activation of class 3 phosphatidylinositol 3OH-kinase
- PMID: 16176982
- PMCID: PMC1242323
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506925102
Amino acids mediate mTOR/raptor signaling through activation of class 3 phosphatidylinositol 3OH-kinase
Abstract
During the evolution of metazoans and the rise of systemic hormonal regulation, the insulin-controlled class 1 phosphatidylinositol 3OH-kinase (PI3K) pathway was merged with the primordial amino acid-driven mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway to control the growth and development of the organism. Insulin regulates mTOR function through a recently described canonical signaling pathway, which is initiated by the activation of class 1 PI3K. However, how the amino acid input is integrated with that of the insulin signaling pathway is unclear. Here we used a number of molecular, biochemical, and pharmacological approaches to address this issue. Unexpectedly, we found that a major pathway by which amino acids control mTOR signaling is distinct from that of insulin and that, instead of signaling through components of the insulin/class 1 PI3K pathway, amino acids mediate mTOR activation by signaling through class 3 PI3K, hVps34.
Figures


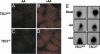

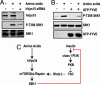
References
-
- Hay, N. & Sonenberg, N. (2004) Genes Dev. 18, 1926-1945. - PubMed
-
- Bjornsti, M. A. & Houghton, P. J. (2004) Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 335-348. - PubMed
-
- Um, S. H., Frigerio, F., Watanabe, M., Picard, F., Joaquin, M., Sticker, M., Fumagalli, S., Allegrini, P. R., Kozma, S. C., Auwerx, J. & Thomas, G. (2004) Nature 431, 200-205. - PubMed
-
- Patti, M. E. & Kahn, B. B. (2004) Nat. Med. 10, 1049-1050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

