Imaging the nanomolar range of nitric oxide with an amplifier-coupled fluorescent indicator in living cells
- PMID: 16176986
- PMCID: PMC1253562
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505136102
Imaging the nanomolar range of nitric oxide with an amplifier-coupled fluorescent indicator in living cells
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Oct 25;102(43):15712
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) is a small uncharged free radical that is involved in diverse physiological and pathophysiological mechanisms. NO is generated by three isoforms of NO synthase, endothelial, neuronal, and inducible ones. When generated in vascular endothelial cells, NO plays a key role in vascular tone regulation, in particular. Here, we describe an amplifier-coupled fluorescent indicator for NO to visualize physiological nanomolar dynamics of NO in living cells (detection limit of 0.1 nM). This genetically encoded high-sensitive indicator revealed that approximately 1 nM of NO, which is enough to relax blood vessels, is generated in vascular endothelial cells even in the absence of shear stress. The nanomolar range of basal endothelial NO thus revealed appears to be fundamental to vascular homeostasis.
Figures
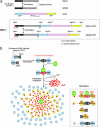
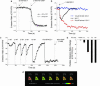
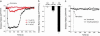
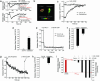
Similar articles
-
Application of Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Nitric Oxide (NO•) Probes, the geNOps, for Real-time Imaging of NO• Signals in Single Cells.J Vis Exp. 2017 Mar 16;(121):55486. doi: 10.3791/55486. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28362417 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescent indicators for Akt/protein kinase B and dynamics of Akt activity visualized in living cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 15;278(33):30945-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212167200. Epub 2003 May 28. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12773546
-
Cell-based indicator to visualize picomolar dynamics of nitric oxide release from living cells.Anal Chem. 2006 Dec 15;78(24):8175-82. doi: 10.1021/ac061791b. Anal Chem. 2006. PMID: 17165805
-
[Mechanisms of nitric oxide synthesis and action in cells].Medicina (Kaunas). 2003;39(6):535-41. Medicina (Kaunas). 2003. PMID: 12829875 Review. Lithuanian.
-
Nitric oxide imaging in living neuronal tissues using fluorescent probes.Nitric Oxide. 2003 Dec;9(4):217-28. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2004.01.001. Nitric Oxide. 2003. PMID: 14996429 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical basis and metabolic interplay of redox regulation.Redox Biol. 2019 Sep;26:101284. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101284. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 31400697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of FRET probes in the analysis of neuronal plasticity.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 Oct 10;7:163. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00163. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 24133415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and development of genetically encoded fluorescent sensors to monitor intracellular chemical and physical parameters.Biophys Rev. 2016 Jun;8(2):121-138. doi: 10.1007/s12551-016-0195-9. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Biophys Rev. 2016. PMID: 28510054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seminaphthofluorescein-based fluorescent probes for imaging nitric oxide in live cells.Inorg Chem. 2011 Oct 3;50(19):9385-92. doi: 10.1021/ic200986v. Epub 2011 Sep 7. Inorg Chem. 2011. PMID: 21895023 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Nitric Oxide (NO•) Probes, the geNOps, for Real-time Imaging of NO• Signals in Single Cells.J Vis Exp. 2017 Mar 16;(121):55486. doi: 10.3791/55486. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28362417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palmer, R. M., Ferrige, A. G. & Moncada, S. (1987) Nature 327, 524-526. - PubMed
-
- Ignarro, L. J. (2000) Nitric Oxide: Biology and Pathobiology (Academic, New York).
-
- Leone, A. M., Furst, V. W., Foxwell, N. A., Cellek, S. & Moncada, S. (1996) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 221, 37-41. - PubMed
-
- Yoshimura, T., Yokoyama, H., Fujii, S., Takayama, F., Oikawa, K. & Kamada, H. (1996) Nat. Biotechnol. 14, 992-994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

