Monoamine oxidase inhibition dramatically increases the motivation to self-administer nicotine in rats
- PMID: 16177026
- PMCID: PMC6725504
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2139-05.2005
Monoamine oxidase inhibition dramatically increases the motivation to self-administer nicotine in rats
Abstract
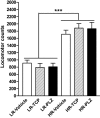
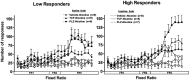
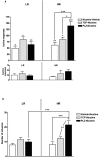
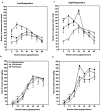
Nicotine is the major neuroactive compound of tobacco, which has, by itself, weak reinforcing properties. It is known that levels of the enzymes monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and MAO-B are reduced in the platelets and brains of smokers and that substances, other than nicotine, present in tobacco smoke have MAO-inhibitory activities. Here, we report that inhibition of MAO dramatically and specifically increases the motivation to self-administer nicotine in rats. These effects were more prominent in rats selected for high responsiveness to novelty than in rats with low responsiveness to novelty. The results suggest that the inhibition of MAO activity by compounds present in tobacco smoke may combine with nicotine to produce the intense reinforcing properties of cigarette smoking that lead to addiction.
Figures



References
-
- Baker GB, Wong JT, Yeung JM, Coutts RT (1991) Effects of the antidepressant phenelzine on brain levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). J Affect Disord 21: 207–211. - PubMed
-
- Berlin I, Anthenelli RM (2001) Monoamine oxidases and tobacco smoking. J Int Neuropsychopharmacol 4: 33–42. - PubMed
-
- Berlin I, Said S, Spreux-Varoquaux O, Olivares R, Launay JM, Puech AJ (1995) Monoamine oxidase A and B activities in heavy smokers. Biol Psychiatry 38: 756–761. - PubMed
-
- Blier P, De Montigny C, Azzaro AJ (1986) Modification of serotonergic and noradrenergic neurotransmissions by repeated administration of monoamine oxidase inhibitors: electrophysiological studies in the rat central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 237: 987–994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
