The ventral pallidum and hedonic reward: neurochemical maps of sucrose "liking" and food intake
- PMID: 16177031
- PMCID: PMC6725525
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1902-05.2005
The ventral pallidum and hedonic reward: neurochemical maps of sucrose "liking" and food intake
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2005 Oct 12;25(41):9554
Abstract
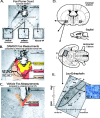
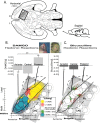
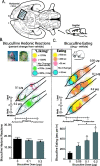
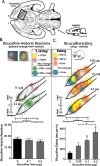
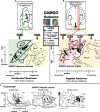
How are natural reward functions such as sucrose hedonic impact and the motivation to eat generated within the ventral pallidum (VP)? Here, we used a novel microinjection and functional mapping procedure to neuroanatomically localize and neurochemically characterize substrates in the VP that mediate increases in eating behavior and enhancements in taste hedonic "liking" reactions. The mu-opioid agonist D-Ala2-N-Me-Phe4-Glycol5-enkephalin (DAMGO) caused increased hedonic "liking" reactions to sucrose only in the posterior VP but conversely suppressed "liking" reactions in the anterior and central VP. DAMGO similarly stimulated eating behavior in the posterior and central VP and suppressed eating in the anterior VP. In contrast, the GABAA antagonist bicuculline increased eating behavior at all VP sites, yet completely failed to enhance sucrose "liking" reactions at any site. These results reveal that VP generation of increased food reward and increased eating behavior is related but dissociable. Hedonic "liking" and eating are systematically mapped in a neuroanatomically and neurochemically interactive manner in the VP.
Figures

References
-
- Abe S, Suzuki T, Endo K, Hori T, Arai H (2005) Effects of single and repeated phencyclidine administration on [3H]flunitrazepam binding in rat brain. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29: 133–140. - PubMed
-
- Bengtson CP, Osborne PB (1999) Electrophysiological properties of anatomically identified ventral pallidal neurons in rat brain slices. Ann NY Acad Sci 877: 691–694. - PubMed
-
- Bengtson CP, Osborne PB (2000) Electrophysiological properties of cholinergic and noncholinergic neurons in the ventral pallidal region of the nucleus basalis in rat brain slices. J Neurophysiol 83: 2649–2660. - PubMed
-
- Berridge KC (2000) Measuring hedonic impact in animals and infants: microstructure of affective taste reactivity patterns. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24: 173–198. - PubMed
-
- Berridge KC (2003) Pleasures of the brain. Brain Cogn 52: 106–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
