Proprioceptor regulation of motor circuit activity by presynaptic inhibition of a modulatory projection neuron
- PMID: 16177049
- PMCID: PMC6510986
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2663-05.2005
Proprioceptor regulation of motor circuit activity by presynaptic inhibition of a modulatory projection neuron
Abstract
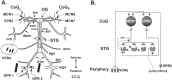
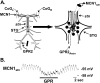
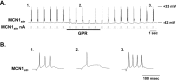
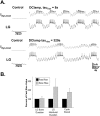
Phasically active sensory systems commonly influence rhythmic motor activity via synaptic actions on the relevant circuit and/or motor neurons. Using the crab stomatogastric nervous system (STNS), we identified a distinct synaptic action by which an identified proprioceptor, the gastropyloric muscle stretch receptor (GPR) neuron, regulates the gastric mill (chewing) motor rhythm. Previous work showed that rhythmically stimulating GPR in a gastric mill-like pattern, in the isolated STNS, elicits the gastric mill rhythm via its activation of two identified projection neurons, modulatory commissural neuron 1 (MCN1) and commissural projection neuron 2, in the commissural ganglia. Here, we determine how activation of GPR with a behaviorally appropriate pattern (active during each gastric mill retractor phase) influences an ongoing gastric mill rhythm via actions in the stomato gastric ganglion, where the gastric mill circuit is located. Stimulating GPR during each retractor phase selectively prolongs that phase and thereby slows the ongoing rhythm. This selective action on the retractor phase results from two distinct GPR actions. First, GPR presynaptically inhibits the axon terminals of MCN1, reducing MCN1 excitation of all gastric mill neurons. Second, GPR directly excites the retractor phase neurons. Because MCN1 transmitter release occurs during each retractor phase, these parallel GPR actions selectively reduce the buildup of excitatory drive to the protractor phase neurons, delaying each protractor burst. Thus, rhythmic proprioceptor feedback to a motor circuit can result from a global reduction in excitatory drive to that circuit, via presynaptic inhibition, coupled with a phase-specific excitatory input that prolongs the excited phase by delaying the onset of the subsequent phase.
Figures








References
-
- Beenhakker MP (2004) Sensory regulation of rhythmically active neuronal networks. PhD thesis, University of Pennsylvania.
-
- Beenhakker MP, Nusbaum MP (2003) Sensory regulation of a modulatory projection neuron at two separate locations. Soc Neurosci Abstr 29: 604.11.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
