Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) modulates amyloid precursor protein cleavage and reduces cerebral amyloidosis in Alzheimer transgenic mice
- PMID: 16177050
- PMCID: PMC6725500
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1521-05.2005
Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) modulates amyloid precursor protein cleavage and reduces cerebral amyloidosis in Alzheimer transgenic mice
Abstract
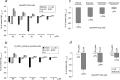
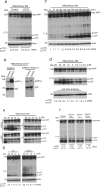
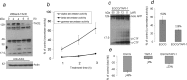
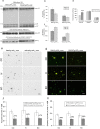
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder pathologically characterized by deposition of beta-amyloid (Abeta) peptides as senile plaques in the brain. Recent studies suggest that green tea flavonoids may be used for the prevention and treatment of a variety of neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we report that (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), the main polyphenolic constituent of green tea, reduces Abeta generation in both murine neuron-like cells (N2a) transfected with the human "Swedish" mutant amyloid precursor protein (APP) and in primary neurons derived from Swedish mutant APP-overexpressing mice (Tg APPsw line 2576). In concert with these observations, we find that EGCG markedly promotes cleavage of the alpha-C-terminal fragment of APP and elevates the N-terminal APP cleavage product, soluble APP-alpha. These cleavage events are associated with elevated alpha-secretase activity and enhanced hydrolysis of tumor necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme, a primary candidate alpha-secretase. As a validation of these findings in vivo, we treated Tg APPsw transgenic mice overproducing Abeta with EGCG and found decreased Abeta levels and plaques associated with promotion of the nonamyloidogenic alpha-secretase proteolytic pathway. These data raise the possibility that EGCG dietary supplementation may provide effective prophylaxis for AD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ADAM10 activation is required for green tea (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced alpha-secretase cleavage of amyloid precursor protein.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jun 16;281(24):16419-27. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600617200. Epub 2006 Apr 19. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16624814
-
Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces beta-amyloid mediated cognitive impairment and modulates tau pathology in Alzheimer transgenic mice.Brain Res. 2008 Jun 12;1214:177-87. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.107. Epub 2008 Apr 7. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18457818
-
Octyl gallate markedly promotes anti-amyloidogenic processing of APP through estrogen receptor-mediated ADAM10 activation.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 15;8(8):e71913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071913. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23977176 Free PMC article.
-
Green Tea Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) Targeting Protein Misfolding in Drug Discovery for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biomolecules. 2021 May 20;11(5):767. doi: 10.3390/biom11050767. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34065606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of (-)-Epigallo-catechin-(3)-gallate on Amyloidogenic Proteins Suggests a Common Mechanism.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;863:139-61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-18365-7_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26092630 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Compounds as Inhibitors of Aβ Peptide and Tau Aggregation.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(10):1234-1250. doi: 10.2174/0118715273273539231114095300. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38018200 Review.
-
Chemical Profiling and Dose-Dependent Assessment of Fear Reducing and Memory-Enhancing Effects of Solanum virginianum in Rats.Dose Response. 2021 Mar 4;19(1):1559325821998486. doi: 10.1177/1559325821998486. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. Dose Response. 2021. PMID: 33746655 Free PMC article.
-
EGCG functions through estrogen receptor-mediated activation of ADAM10 in the promotion of non-amyloidogenic processing of APP.FEBS Lett. 2010 Oct 8;584(19):4259-67. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.09.022. Epub 2010 Sep 17. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20849853 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits of dietary polyphenols in Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Dec 13;14:1019942. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1019942. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36583187 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbenante G, Kovacs DM, Leung DL, Craik DJ, Tanzi RE, Fairlie DP (2000) Inhibitors of beta-amyloid formation based on the beta-secretase cleavage site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 268: 133–135. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S, Rahman A, Hasnain A, Lalonde M, Goldberg VM, Haqqi TM (2002) Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the IL-1 beta-induced activity and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and nitric oxide synthase-2 in human chondrocytes. Free Radic Bio Med 33: 1097–1105. - PubMed
-
- Aktas O, Prozorovski T, Smorodchenko A, Savaskan NE, Lauster R, Kloetzel PM, Infante-Duarte C, Brocke S, Zipp F (2004) Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate mediates T cellular NF-kappaB inhibition and exerts neuroprotection in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 173: 5794–5800. - PubMed
-
- Allinson TM, Parkin ET, Turner AJ, Hooper NM (2003) ADAMs family members as amyloid precursor protein alpha-secretases. J Neurosci Res 74: 342–352. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan NB, Siegel GJ (2003) Intracerebroventricular passive immunization with anti-Abeta antibody in Tg2576. J Neurosci Res 74: 142–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
