Dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3-grabbing nonintegrin/CD209 is abundant on macrophages in the normal human lymph node and is not required for dendritic cell stimulation of the mixed leukocyte reaction
- PMID: 16177066
- PMCID: PMC1378112
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.7.4265
Dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3-grabbing nonintegrin/CD209 is abundant on macrophages in the normal human lymph node and is not required for dendritic cell stimulation of the mixed leukocyte reaction
Abstract
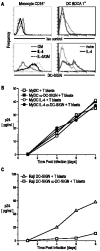
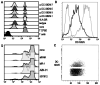
The C-type lectin dendritic cell-specific ICAM 3-grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN)/CD209 efficiently binds several pathogens, including HIV-1. DC-SIGN is expressed on monocyte-derived DCs in culture, and importantly, it is able to sequester HIV-1 within cells and facilitate transmission of virus to CD4+ T cells. To investigate DC-SIGN function, we have generated new mAbs. We report in this study that these and prior anti-DC-SIGN mAbs primarily label macrophages in the medullary sinuses of noninflamed human lymph node. In contrast, expression is not detected on most DCs in the T cell area, except for occasional cells. We also noted that IL-4 alone can induce expression of DC-SIGN in CD14+ monocytes and circulating blood DCs. However, blockade of DC-SIGN with Abs and DC-SIGN small interfering RNA did not result in a major reduction in the capacity of these DCs to transfer HIV to T cells, confirming significant DC-SIGN-independent mechanisms. The blocking approaches did reduce HIV-1 transmission by DC-SIGN-transfected cells by >90%. DC-SIGN blockade also did not reduce the ability of DCs to stimulate T cell proliferation in the MLR. These results indicate that DC-SIGN has the potential to contribute to macrophage function in normal human lymph node, and that DCs do not require DC-SIGN to transmit HIV or to initiate T cell responses.
Figures

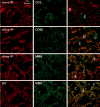
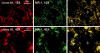
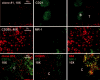
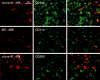
References
-
- Geijtenbeek TBH, Torensma R, van Vliet SJ, van Duijnhoven GCF, Adema GJ, van Kooyk Y, Figdor CG. Identification of DC-SIGN, a novel dendritic cell-specific ICAM-3 receptor that supports primary immune responses. Cell. 2000;100:575–585. - PubMed
-
- Van Kooyk Y, Geijtenbeek TB. DC-SIGN: escape mechanism for pathogens. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:697–709. - PubMed
-
- Geijtenbeek TB, Kwon DS, Torensma R, van Vliet SJ, van Duijnhoven GC, Middel J, Cornelissen IL, Nottet HS, KewalRamani VN, Littman DR, et al. DC-SIGN, a dendritic cell specific HIV-1 binding protein that enhances TRANS-infection of T cells. Cell. 2000;100:587–597. - PubMed
-
- Kwon DS, Gregario G, Bitton N, Hendrickson WA, Littman DR. DC-SIGN mediated internalization of HIV is required for trans-enhancement of T cell infection. Immunity. 2002;16:135–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

