Identification of new secreted effectors in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 16177297
- PMCID: PMC1230965
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6260-6271.2005
Identification of new secreted effectors in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
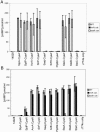
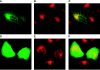
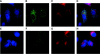
A common theme in bacterial pathogenesis is the secretion of bacterial products that modify cellular functions to overcome host defenses. Gram-negative bacterial pathogens use type III secretion systems (TTSSs) to inject effector proteins into host cells. The genes encoding the structural components of the type III secretion apparatus are conserved among bacterial species and can be identified by sequence homology. In contrast, the sequences of secreted effector proteins are less conserved and are therefore difficult to identify. A strategy was developed to identify virulence factors secreted by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium into the host cell cytoplasm. We constructed a transposon, which we refer to as mini-Tn5-cycler, to generate translational fusions between Salmonella chromosomal genes and a fragment of the calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase gene derived from Bordetella pertussis (cyaA'). In-frame fusions to bacterial proteins that are secreted into the eukaryotic cell cytoplasm were identified by high levels of cyclic AMP in infected cells. The assay was sufficiently sensitive that a single secreted fusion could be identified among several hundred that were not secreted. This approach identified three new effectors as well as seven that have been previously characterized. A deletion of one of the new effectors, steA (Salmonella translocated effector A), attenuated virulence. In addition, SteA localizes to the trans-Golgi network in both transfected and infected cells. This approach has identified new secreted effector proteins in Salmonella and will likely be useful for other organisms, even those in which genetic manipulation is more difficult.
Figures


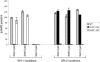
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M. 1987. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates, Brooklyn, N.Y.
-
- Bajaj, V., R. L. Lucas, C. Hwang, and C. A. Lee. 1996. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol. Microbiol. 22:703-714. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J., K. S. de Felipe, M. Clarke, H. Lu, O. R. Anderson, G. Segal, and H. A. Shuman. 2004. Legionella effectors that promote nonlytic release from protozoa. Science 303:1358-1361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

