Activation and mitogen-activated protein kinase regulation of transcription factors Ets and NF-kappaB in Mycobacterium-infected macrophages and role of these factors in tumor necrosis factor alpha and nitric oxide synthase 2 promoter function
- PMID: 16177323
- PMCID: PMC1230939
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6499-6507.2005
Activation and mitogen-activated protein kinase regulation of transcription factors Ets and NF-kappaB in Mycobacterium-infected macrophages and role of these factors in tumor necrosis factor alpha and nitric oxide synthase 2 promoter function
Abstract
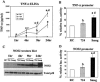
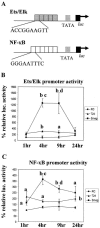
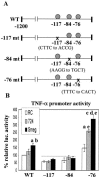
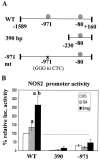
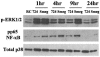
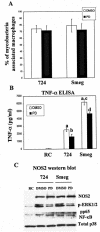
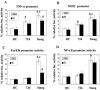
Previous studies have shown that primary murine macrophages infected with Mycobacterium avium produced lower levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and inducible nitric oxide synthase 2 (NOS2) compared to cells infected with nonpathogenic Mycobacterium smegmatis. TNF-alpha and NOS2 levels correlated with and were dependent on the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). To define the macrophage transcriptional responses dependent on ERK1/2 activation following a mycobacterial infection, we used RAW 264.7 cells transfected with a TNF-alpha or NOS2 promoter vector. We determined that macrophages infected with M. avium compared to M. smegmatis showed diminished TNF-alpha and NOS2 promoter activity. A more pronounced difference in promoter activity was observed when only the consensus ETS and NF-kappaB binding sites were used as promoters. Mutational analysis of the ETS and NF-kappaB binding sites present on the TNF-alpha and NOS2 promoters, respectively, showed that these sites were essential for a functional promoter. Moreover, the Ets/Elk but not the NF-kappaB transcriptional response was dependent on ERK1/2. This correlated with the requirement for ERK1/2 in TNF-alpha but not NOS2 promoter activity. Our data indicate that the increased Ets/Elk and NF-kappaB promoter activities associated with M. smegmatis-infected macrophages are responsible, at least in part, for the increased TNF-alpha and NOS2 production observed in these infected cells and that ERK1/2 is required for Ets/Elk activity and full TNF-alpha production.
Figures

References
-
- Baldwin, A. S., Jr. 1996. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:649-683. - PubMed
-
- Barthel, R., A. V. Tsytsykova, A. K. Barczak, E. Y. Tsai, C. C. Dascher, M. B. Brenner, and A. E. Goldfeld. 2003. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression by mycobacteria involves the assembly of a unique enhanceosome dependent on the coactivator proteins CBP/p300. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23:526-533. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bermudez, L. E., and L. S. Young. 1988. Tumor necrosis factor, alone or in combination with IL-2, but not IFN-gamma, is associated with macrophage killing of Mycobacterium avium complex. J. Immunol. 140:3006-3013. - PubMed
-
- Chan, E. D., K. R. Morris, J. T. Belisle, P. Hill, L. K. Remigio, P. J. Brennan, and D. W. Riches. 2001. Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase-NO* by lipoarabinomannan of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is mediated by MEK1-ERK, MKK7-JNK, and NF-κB signaling pathways. Infect. Immun. 69:2001-2010. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

