Clearance of Bordetella parapertussis from the lower respiratory tract requires humoral and cellular immunity
- PMID: 16177324
- PMCID: PMC1230969
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6508-6513.2005
Clearance of Bordetella parapertussis from the lower respiratory tract requires humoral and cellular immunity
Abstract
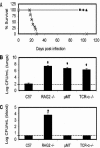
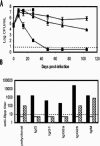
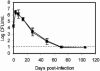
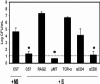
Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella pertussis are closely related species that cause whooping cough, an acute, immunizing disease. Their coexistence in the same host populations at the same time and vaccine studies showing that B. pertussis vaccines have little effect on B. parapertussis infection or disease suggest that the protective immunity induced by each does not efficiently cross protect against the other. Although the mechanisms of protective immunity to B. pertussis have been well studied, those of B. parapertussis have not. The present study explores the mechanism by which B. parapertussis is cleared from the lower respiratory tract by anamnestic immunity. Serum antibodies are necessary and sufficient for elimination of this bacterium, and CD4(+) T cells, complement, and neutrophils are required for serum antibody-mediated clearance. Mice lacking immunoglobulin A had no defect in their ability to control or clear infection. Interestingly, serum antibody-mediated clearance of B. parapertussis did not require Fc receptors that are required for antibody-mediated clearance of B. pertussis. Together these data support a model for the mechanism of protective immunity to B. parapertussis that is similar but distinct from that of B. pertussis.
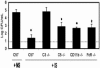
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of systemic and mucosal immune responses in reciprocal protection against Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis in a murine model of respiratory infection.Infect Immun. 2003 Feb;71(2):733-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.733-738.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12540552 Free PMC article.
-
The O antigen enables Bordetella parapertussis to avoid Bordetella pertussis-induced immunity.Infect Immun. 2007 Oct;75(10):4972-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00763-07. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17698566 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal protective immunity against Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis in a murine model of respiratory infection.Infect Immun. 2001 Nov;69(11):6981-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.6981-6986.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11598073 Free PMC article.
-
Other Bordetellas, lessons for and from pertussis vaccines.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014 Sep;13(9):1125-33. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2014.942221. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014. PMID: 25034039 Review.
-
Bordetella pertussis, B. parapertussis, vaccines and cycles of whooping cough.Pathog Dis. 2015 Oct;73(7):ftv055. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv055. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26242280 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Immune Cell Differences Associated With Low Vaccine Responses in Infants.J Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 15;213(12):2014-9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiw053. Epub 2016 Feb 9. J Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26908730 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative role of immunoglobulin A in protective immunity against the Bordetellae.Infect Immun. 2007 Sep;75(9):4416-22. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00412-07. Epub 2007 Jun 25. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17591791 Free PMC article.
-
β-Defensins Coordinate In Vivo to Inhibit Bacterial Infections of the Trachea.Vaccines (Basel). 2018 Aug 28;6(3):57. doi: 10.3390/vaccines6030057. Vaccines (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30154362 Free PMC article.
-
O antigen allows B. parapertussis to evade B. pertussis vaccine-induced immunity by blocking binding and functions of cross-reactive antibodies.PLoS One. 2009 Sep 14;4(9):e6989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006989. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19750010 Free PMC article.
-
The O antigen is a critical antigen for the development of a protective immune response to Bordetella parapertussis.Infect Immun. 2009 Nov;77(11):5050-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00667-09. Epub 2009 Sep 8. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19737902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, A. G., R. M. Thomas, J. T. Cadisch, and D. J. Maskill. 1998. Molecular and functional analysis of the lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis locus wlb from Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Mol. Microbiol. 29:27-38. - PubMed
-
- Borska, K., and M. Simkovicova. 1972. Studies on the circulation of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis in populations of children. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 16:159-172. - PubMed
-
- Circolo, A., G. Garnier, W. Fukuda, X. Wang, T. Hidvegi, A. J. Szalai, D. E. Briles, J. E. Volanakis, R. S. Wetsel, and H. R. Colten. 1999. Genetic disruption of the murine complement C3 promoter region generates deficient mice with extrahepatic expression of C3 mRNA. Immunopharmacology 42:135-149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

