The chemokine CCL2 is required for control of murine gastric Salmonella enterica infection
- PMID: 16177325
- PMCID: PMC1230974
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6514-6522.2005
The chemokine CCL2 is required for control of murine gastric Salmonella enterica infection
Abstract
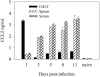
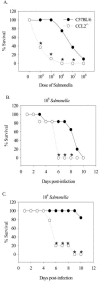
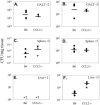
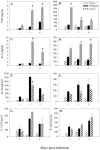
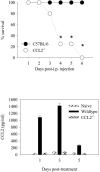
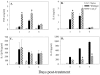
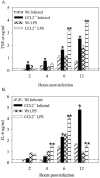
Salmonella enterica is a gram-negative intracellular pathogen that can cause a variety of diseases ranging from gastroenteritis to typhoid fever. The Typhimurium serotype causes gastroenteritis in humans; however, infection of mice results in an enteric fever that resembles human typhoid fever and has been used as a model for typhoid fever. The present study examined the role of the chemokine CCL2 in the control of Salmonella infection. Upon infection with salmonellae, mucosal expression of CCL2 is rapidly up-regulated, followed by systemic expression in the spleen. CCL2(-/-) mice became moribund earlier and had a higher rate of mortality compared to wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Moreover, CCL2(-/-) mice had significantly higher levels of bacteria in the liver compared to wild-type controls. Mucosal and serum interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha levels were elevated in CCL2(-/-) mice compared to wild-type mice. In vitro analysis demonstrated that CCL2(-/-) macrophages infected with salmonellae resulted in dysregulated cytokine production compared to macrophages derived from wild-type mice. These data are the first to directly demonstrate CCL2 as a critical factor for immune responses and survival following S. enterica infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salmonella infections in the absence of the major histocompatibility complex II.J Leukoc Biol. 1998 Mar;63(3):297-304. doi: 10.1002/jlb.63.3.297. J Leukoc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9500516
-
Murein lipoprotein is a critical outer membrane component involved in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium systemic infection.Infect Immun. 2005 Feb;73(2):1081-96. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.2.1081-1096.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15664952 Free PMC article.
-
Activation, cytokine production, and intracellular survival of bacteria in Salmonella-infected human monocyte-derived macrophages and dendritic cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2005 Oct;78(4):909-20. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1204721. Epub 2005 Jul 20. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. PMID: 16033811
-
Caveolin-1-deficient mice show defects in innate immunity and inflammatory immune response during Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection.Infect Immun. 2006 Dec;74(12):6665-74. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00949-06. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16982844 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the genes for ClpXP protease in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium results in persistent infection in mice, and development of persistence requires endogenous gamma interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha.Infect Immun. 2001 May;69(5):3164-74. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.5.3164-3174.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11292737 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Low plasma levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in patients with alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency-related fibromyalgia.Clin Rheumatol. 2010 Feb;29(2):189-97. doi: 10.1007/s10067-009-1318-5. Epub 2009 Nov 19. Clin Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 19924498
-
Therapeutic delivery of CCL2 modulates immune response and restores host-microbe homeostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Sep 3;121(36):e2400528121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2400528121. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39186644 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal stress causes intrauterine inflammation and serotonergic dysfunction, and long-term behavioral deficits through microbe- and CCL2-dependent mechanisms.Transl Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 16;10(1):191. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-00876-5. Transl Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32546752 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine-induced inflammation and inflammatory monocytes promote CD4+ T cell-dependent immunity against murine salmonellosis.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Sep 21;19(9):e1011666. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011666. eCollection 2023 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37733817 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella-host interactions - modulation of the host innate immune system.Front Immunol. 2014 Oct 7;5:481. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00481. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25339955 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barsig, J., S. Kusters, K. Vogt, H. D. Volk, G. Tiegs, and A. Wendel. 1995. Lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-10 in mice: role of endogenous tumor necrosis factor alpha. Eur. J. Immunol. 25:2888-2893. - PubMed
-
- Bossink, A. W., L. Paemen, P. M. Jansen, C. E. Hack, L. G. Thijs, and J. Van Damme. 1995. Plasma levels of the chemokines monocyte chemotactic proteins-1 and -2 are elevated in human sepsis. Blood 86:3841-3847. - PubMed
-
- Braun, M. C., E. Lahey, and B. L. Kelsall. 2000. Selective suppression of IL-12 production by chemoattractants. J. Immunol. 164:3009-3017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

