Recombinant Shiga toxin B-subunit-keyhole limpet hemocyanin conjugate vaccine protects mice from Shigatoxemia
- PMID: 16177326
- PMCID: PMC1230940
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6523-6529.2005
Recombinant Shiga toxin B-subunit-keyhole limpet hemocyanin conjugate vaccine protects mice from Shigatoxemia
Abstract
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) causes hemorrhagic colitis in humans and, in a subgroup of infected subjects, a more serious condition called hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS). These conditions arise because EHEC produces two antigenically distinct forms of Shiga toxin (Stx), called Stx1 and Stx2. Despite this, the production of Stx2 by virtually all EHEC serotypes and the documented role this toxin plays in HUS make it an attractive vaccine candidate. Previously, we assessed the potential of a purified recombinant Stx2 B-subunit preparation to prevent Shigatoxemia in rabbits. This study revealed that effective immunization could be achieved only if endotoxin was included with the vaccine antigen. Since the presence of endotoxin would be unacceptable in a human vaccine, the object of the studies described herein was to investigate ways to safely augment, in mice, the immunogenicity of the recombinant Stx2 B subunit containing <1 endotoxin unit per ml. The study revealed that sera from mice immunized with such a preparation, conjugated to keyhole limpet hemocyanin and administered with the Ribi adjuvant system, displayed the highest Shiga toxin 2 B-subunit-specific immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) and IgG2a enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay titers and cytotoxicity-neutralizing activities in Ramos B cells. As well, 100% of the mice vaccinated with this preparation were subsequently protected from a lethal dose of Stx2 holotoxin. These results support further evaluation of a Stx2 B-subunit-based human EHEC vaccine.
Figures

 ), Quil A plus LPS (- - - - ), Alhydrogel (...), Alhydrogel plus MPL (—), RAS-TDM (), and RAS-TDM plus MPL (
), Quil A plus LPS (- - - - ), Alhydrogel (...), Alhydrogel plus MPL (—), RAS-TDM (), and RAS-TDM plus MPL ( ). (A) Groups of five mice were used per immunization protocol; (B) groups of 15 mice were used per immunization protocol.
). (A) Groups of five mice were used per immunization protocol; (B) groups of 15 mice were used per immunization protocol.

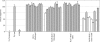

 ), Stx2 B-subunit-KLH mixed with Alhydrogel (—), KLH mixed with RAS-TDM (- - -), and Stx2 B-subunit-KLH mixed with RAS-TDM (). The differences in the survival rates of mice immunized with the Stx2 B-subunit-KLH conjugate preparations and those of the mice immunized with KLH alone were highly significant (P = 0.025 and 0.011, Stx2 B-subunit-KLH administered with Alhydrogel or RAS-TDM, respectively, Fisher's exact test).
), Stx2 B-subunit-KLH mixed with Alhydrogel (—), KLH mixed with RAS-TDM (- - -), and Stx2 B-subunit-KLH mixed with RAS-TDM (). The differences in the survival rates of mice immunized with the Stx2 B-subunit-KLH conjugate preparations and those of the mice immunized with KLH alone were highly significant (P = 0.025 and 0.011, Stx2 B-subunit-KLH administered with Alhydrogel or RAS-TDM, respectively, Fisher's exact test).Similar articles
-
Immunoprophylactic potential of cloned Shiga toxin 2 B subunit.J Infect Dis. 2001 Feb 1;183(3):435-43. doi: 10.1086/318080. Epub 2000 Dec 27. J Infect Dis. 2001. PMID: 11133375
-
Large-scale preparation of Shiga toxin 2 in Escherichia coli for toxoid vaccine antigen production.Microbiol Immunol. 2013 Jan;57(1):38-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2012.12004.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23157558
-
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli trivalent recombinant vaccine containing EspA, intimin and Stx2 induces strong humoral immune response and confers protection in mice.Microbes Infect. 2009 Sep;11(10-11):835-41. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2009.04.024. Epub 2009 May 7. Microbes Infect. 2009. PMID: 19427397
-
[Development of vaccine for enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli infection].Nihon Rinsho. 2002 Jun;60(6):1083-8. Nihon Rinsho. 2002. PMID: 12078077 Review. Japanese.
-
Construction of a novel bioluminescent reporter system for investigating Shiga toxin expression of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Gene. 2011 Jun 1;478(1-2):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2011.01.006. Epub 2011 Jan 22. Gene. 2011. PMID: 21262333 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibodies anti-Shiga toxin 2 B subunit from chicken egg yolk: isolation, purification and neutralization efficacy.Toxicon. 2011 Sep 15;58(4):380-8. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2011.07.009. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Toxicon. 2011. PMID: 21803069 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion expression and immunogenicity of EHEC EspA-Stx2Al protein: implications for the vaccine development.J Microbiol. 2009 Aug;47(4):498-505. doi: 10.1007/s12275-009-0116-8. Epub 2009 Sep 9. J Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19763426
-
Antibody responses elicited in mice immunized with Bacillus subtilis vaccine strains expressing Stx2B subunit of enterohaemorragic Escherichia coli O157:H7.Braz J Microbiol. 2009 Apr;40(2):333-8. doi: 10.1590/S1517-838220090002000023. Epub 2009 Jun 1. Braz J Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 24031368 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccines for viral and bacterial pathogens causing acute gastroenteritis: Part II: Vaccines for Shigella, Salmonella, enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) enterohemorragic E. coli (EHEC) and Campylobacter jejuni.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(3):601-19. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1011578. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25715096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Live attenuated Shigella dysenteriae type 1 vaccine strains overexpressing shiga toxin B subunit.Infect Immun. 2011 Dec;79(12):4912-22. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05814-11. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21969003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armstrong, G. D., P. N. McLaine, and P. C. Rowe. 1998. Clinical trials of Synsorb-Pk in preventing hemolytic-uremic syndrome, p. 374-384. In J. B. Kaper and A. D. O'Brien (ed.), Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other Shiga toxin-producing E. coli strains. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

