Mediation of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-LP transcriptional coactivation by Sp100
- PMID: 16177824
- PMCID: PMC1276704
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600820
Mediation of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-LP transcriptional coactivation by Sp100
Abstract
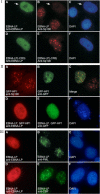
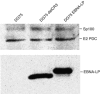
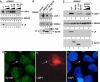
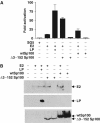
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) EBNA-LP protein is important for EBV-mediated B-cell immortalization and is a potent gene-specific coactivator of the viral transcriptional activator, EBNA2. The mechanism(s) by which EBNA-LP functions as a coactivator remains an important question in the biology of EBV-induced B-cell immortalization. In this study, we found that EBNA-LP interacts with the promyelocytic leukemia nuclear body (PML NB)-associated protein Sp100 and displaces Sp100 and heterochromatin protein 1alpha (HP1alpha) from PML NBs. Interaction between EBNA-LP and Sp100 was mediated through conserved region 3 in EBNA-LP and the PML NB targeting domain in Sp100. Overexpression of Sp100 lacking the N-terminal PML NB targeting domain, but not a mutant form of Sp100 lacking the HP1alpha interaction domain, was sufficient to coactivate EBNA2 in a gene-specific manner independent of EBNA-LP. These findings suggest that Sp100 is a major mediator of EBNA-LP coactivation. These studies indicate that modulation of PML NB-associated proteins may be important for establishment of latent viral infections, and also identify a convenient model system to investigate the functions of Sp100.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of Sp100A subnuclear localization and transcriptional function by EBNA-LP and interferon.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008 Nov;28(11):667-78. doi: 10.1089/jir.2008.0023. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008. PMID: 18844582 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-LP protein preferentially coactivates EBNA2-mediated stimulation of latent membrane proteins expressed from the viral divergent promoter.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(7):4492-505. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4492-4505.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15767449 Free PMC article.
-
Protein kinase A associates with HA95 and affects transcriptional coactivation by Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;22(7):2136-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.7.2136-2146.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11884601 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling is not required for the Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-LP transcriptional coactivation function.J Virol. 2009 Jul;83(14):7109-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00654-09. Epub 2009 Apr 29. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19403674 Free PMC article.
-
EBNA2 and Its Coactivator EBNA-LP.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:35-59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_2. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26428371 Review.
Cited by
-
The Fate of Speckled Protein 100 (Sp100) During Herpesviruses Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Feb 1;10:607526. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.607526. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33598438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Murine gammaherpesvirus 68 open reading frame 75c tegument protein induces the degradation of PML and is essential for production of infectious virus.J Virol. 2008 Aug;82(16):8000-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02752-07. Epub 2008 May 28. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18508901 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Herpesvirus Infection and Host Defense by PML Nuclear Bodies.Viruses. 2009 Dec;1(3):1240-64. doi: 10.3390/v1031240. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Viruses. 2009. PMID: 21994592 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus EBNA-3C is targeted to and regulates expression from the bidirectional LMP-1/2B promoter.J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(22):11200-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00897-06. Epub 2006 Sep 6. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16956945 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear remodelling during viral infections.Cell Microbiol. 2011 Jun;13(6):806-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01596.x. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Cell Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21501365 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allan GJ, Inman GJ, Parker BD, Rowe DT, Farrell PJ (1992) Cell growth effects of Epstein–Barr virus leader protein. J Gen Virol 73: 1547–1551 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

