Clinical uses of intravenous immunoglobulin
- PMID: 16178850
- PMCID: PMC1809480
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02834.x
Clinical uses of intravenous immunoglobulin
Figures
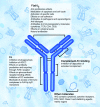
References
-
- Imbach P, Barandun S, d’Apuzzo V, et al. High-dose intravenous gammaglobulin for idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in childhood. Lancet. 1981;1:1228–31. - PubMed
-
- Lamari F, Anastassiou ED, Tsegenidis T, et al. An enzyme immunoassay to determine the levels of specific antibodies toward bacterial surface antigens in human immunoglobulin preparations and blood serum. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1999;20:913–20. - PubMed
-
- Kawada K, Terasaki PI. Evidence for immunosuppression by high-dose gammaglobulin. Exp Hematol. 1987;15:133–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

