The beta1 adrenergic effects of antibodies against the C-terminal end of the ribosomal P2beta protein of Trypanosoma cruzi associate with a specific pattern of epitope recognition
- PMID: 16178868
- PMCID: PMC1809475
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02885.x
The beta1 adrenergic effects of antibodies against the C-terminal end of the ribosomal P2beta protein of Trypanosoma cruzi associate with a specific pattern of epitope recognition
Abstract
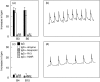
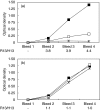
BALB/c mice immunized with recombinant Trypanosoma cruzi ribosomal P2beta protein (TcP2beta) develop a strong and specific antibody response against its 13 residue-long C-terminal epitope (peptide R13: EEEDDDMGFGLFD) that has a concomitant beta1-adrenergic stimulating activity. However, other animals that undergo similar immunizations seem tolerant to this epitope. To evaluate further the antibody response against the ribosomal P proteins, 25 BALB/c and 25 Swiss mice were immunized with TcP2beta. From the 50 animals, 31 developed a positive anti-R13 response, whereas 19 were non-responsive. From the 31 anti-R13 positive mice, 25 had anti-R13 antibodies that recognized the discontinuous motif ExDDxGF, and their presence correlated with the recording of supraventricular tachycardia. The other six had anti-R13 antibodies but with a normal electrocardiographic recording. These anti-R13 antibodies recognized the motif DDxGF shared by mammals and T. cruzi and proved to be a true anti-P autoantibody because they were similar to those elicited in Swiss, but not in BALB/c mice, by immunization with the C-terminal portion of the mouse ribosomal P protein. Our results show that the recognition of the glutamic acid in position 3 of peptide R13 defines the ability of anti-R13 antibodies to react with the motif AESDE of the second extracellular loop of the beta1-adrenergic receptor, setting the molecular basis for their pathogenic beta1 adrenoceptor stimulating activity.
Figures
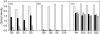
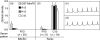

Similar articles
-
Antibodies against the carboxyl-terminal end of the Trypanosoma cruzi ribosomal P proteins are pathogenic.FASEB J. 2001 Dec;15(14):2602-12. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0132com. FASEB J. 2001. PMID: 11726536
-
Structural basis of the cross-reaction between an antibody to the Trypanosoma cruzi ribosomal P2beta protein and the human beta1 adrenergic receptor.FASEB J. 2006 Jul;20(9):1396-406. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-5699com. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16816115
-
A monoclonal antibody against the immunodominant epitope of the ribosomal P2beta protein of Trypanosoma cruzi interacts with the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor.Eur J Immunol. 2001 Jul;31(7):2210-6. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200107)31:7<2210::aid-immu2210>3.0.co;2-j. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11449375
-
Humoral autoimmune response in Chagas' disease: Trypanosoma cruzi ribosomal antigens as immunizing agents.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1993 Oct;7(3):205-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1993.tb00400.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1993. PMID: 7506093 Review.
-
Cross-talk between anti-beta1-adrenoceptor antibodies in dilated cardiomyopathy and Chagas' heart disease.Autoimmunity. 2008 Sep;41(6):429-33. doi: 10.1080/08916930802031702. Autoimmunity. 2008. PMID: 18781468 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug-like actions of autoantibodies against receptors of the autonomous nervous system and their impact on human heart function.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;166(3):847-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01828.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22220626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autoantibodies against M5-muscarinic and beta1-adrenergic receptors in periodontitis patients.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Aug 28;12(16):16609-16620. doi: 10.18632/aging.103864. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32857064 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine production but lack of proliferation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from chronic Chagas' disease cardiomyopathy patients in response to T. cruzi ribosomal P proteins.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Jun 5;8(6):e2906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002906. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24901991 Free PMC article.
-
Are anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies relevant in systemic lupus erythematosus?Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2007 Feb;32(1):37-46. doi: 10.1007/BF02686080. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17426359 Review.
-
Anti-beta1-adrenergic receptor autoantibodies in patients with chronic Chagas heart disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 Jun;148(3):440-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03381.x. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17419712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elizari MV, Chiale PA. Pharmacologic treatment of arrhythmias related to chronic Chagas' heart disease. In: Tentori MC, Segura E, Hayes DL, editors. Arrhytmia management in Chagas' disease. Armonk, New York: Futura Publishing Co.; 2000. pp. 95–116.
-
- Chiale PA, Ferrari I, Mahler E, et al. Differential profile and biochemical effects of antiautonomic membrane receptor antibodies in ventricular arrhythmias and sinus node dysfunction. Circulation. 2001;103:1765–71. - PubMed
-
- Borda E, Sterin-Borda L. Antiadrenergic and muscarinic receptor antibodies in Chagas' cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol. 1996;54:149–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

