Cross-recognition between histones and La/SSB may account for anti-DNA reactivity in SLE patients
- PMID: 16178873
- PMCID: PMC1809500
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02892.x
Cross-recognition between histones and La/SSB may account for anti-DNA reactivity in SLE patients
Abstract
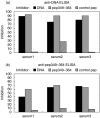
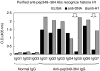
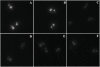
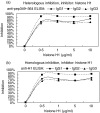
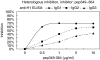
Antibodies to La/SSB are detected in sera of patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome (pSS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The vast majority of anti-La/SSB positive sera contain antibodies directed towards a linear B-cell epitope of La/SSB spanning the sequence 349-364aa (pep349-364). The aim of this study was to evaluate the fluctuation of antibody levels to major B-cell epitopes of La/SSB over time and investigate for their possible crossreactions. Sequential sera from 15 SLE and 15 pSS patients, followed from 3 to 10 years were obtained. All patients with SLE were positive for anti-Ro/SSA, anti-La/SSB and anti-dsDNA antibodies and patients with pSS were positive for anti-Ro/SSA and anti-La/SSB antibodies. Sera from 30 patients with SLE without anti-La/SSB antibodies and 30 healthy individuals served as disease and negative control respectivelly. All sera tested for the presence of anti-pep349-364 antibodies, using a specific ELISA. Specific anti-pep349-364 IgG was purified from sera of SLE patients and evaluated for cross reactivity against dsDNA and histones. In all SLE sera the levels of anti-pep349-364 antibodies varied in time and fluctuated in parallel with anti dsDNA antibodies. Anti-pep349-364 IgG purified from 7 SLE patients. Five out of 7 were found to react with calf thymus DNA in ELISA. All purified (7/7) anti-pep349-364 IgG preparations reacted with histone H1 and failed to produce a positive immunofluorescence pattern in Crithidia luciliae anti-dsDNA assay which lacks histones. Competative inhibition experiments demonstrated that histone H1 could inhibit completely the binding of anti-pep349-364 IgG to pep349-364 while pep349-364 inhibited by 70% the binding of anti-pep349-364 IgG to histone H1. These findings indicate that a subgroup of SLE patients possess cross-reacting anti-histone H1 antibodies and anti-pep349-364 antibodies, which can be faulty considered as anti-dsDNA reactivity in regular ELISA techniques.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Preferential recognition of the phosphorylated major linear B-cell epitope of La/SSB 349-368 aa by anti-La/SSB autoantibodies from patients with systemic autoimmune diseases.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 Jun;144(3):432-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03088.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16734612 Free PMC article.
-
RNA recognition motif (RRM) of La/SSB: the bridge for interparticle spreading of autoimmune response to U1-RNP.Mol Med. 2010 Jan-Feb;16(1-2):19-26. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2009.00106. Epub 2009 Oct 14. Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 19838329 Free PMC article.
-
Unmasking the anti-La/SSB response in sera from patients with Sjogren's syndrome by specific blocking of anti-idiotypic antibodies to La/SSB antigenic determinants.Mol Med. 2002 Jun;8(6):293-305. Mol Med. 2002. PMID: 12428060 Free PMC article.
-
[Anti-SSA/Ro and anti-SSB/La antibodies. What's new?].Ann Med Interne (Paris). 2002 Dec;153(8):520-9. Ann Med Interne (Paris). 2002. PMID: 12610426 Review. French.
-
Fine specificity of the autoimmune response to the Ro/SSA and La/SSB ribonucleoproteins.Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Feb;42(2):199-209. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199902)42:2<199::AID-ANR1>3.0.CO;2-1. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. PMID: 10025913 Review.
Cited by
-
The SSB-positive/SSA-negative antibody profile is not associated with key phenotypic features of Sjögren's syndrome.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Aug;74(8):1557-61. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206683. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 25735642 Free PMC article.
-
The lupus-derived anti-double-stranded DNA IgG contributes to myofibroblast-like phenotype in mesangial cells.J Clin Immunol. 2012 Dec;32(6):1270-8. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9724-x. Epub 2012 Jun 24. J Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22730054
-
Precise Targeting of Autoantigen-Specific B Cells in Lupus Nephritis with Chimeric Autoantibody Receptor T Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 11;25(8):4226. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084226. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673811 Free PMC article.
-
Linker Histone in Diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2017 Jul 18;13(8):1008-1018. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.19891. eCollection 2017. Int J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28924382 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pruijn GJ, Simons FH, van Venrooij WJ. Intracellular localization and nucleocytoplasmic transport of Ro RNP components. Eur J Cell Biol. 1997;74:123–32. - PubMed
-
- Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982;25:1271–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

