The inositol phosphatase SHIP-2 down-regulates FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis in murine macrophages independently of SHIP-1
- PMID: 16179375
- PMCID: PMC1895625
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-1841
The inositol phosphatase SHIP-2 down-regulates FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis in murine macrophages independently of SHIP-1
Abstract
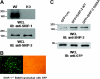
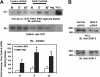
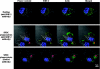
FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis of IgG-coated particles is a complex process involving the activation of multiple signaling enzymes and is regulated by the inositol phosphatases PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10) and SHIP-1 (Src homology [SH2] domain-containing inositol phosphatase). In a recent study we have demonstrated that SHIP-2, an inositol phosphatase with high-level homology to SHIP-1, is involved in FcgammaR signaling. However, it is not known whether SHIP-2 plays a role in modulating phagocytosis. In this study we have analyzed the role of SHIP-2 in FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis using independent cell models that allow for manipulation of SHIP-2 function without influencing the highly homologous SHIP-1. We present evidence that SHIP-2 translocates to the site of phagocytosis and down-regulates FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis. Our data indicate that SHIP-2 must contain both the N-terminal SH2 domain and the C-terminal proline-rich domain to mediate its inhibitory effect. The effect of SHIP-2 is independent of SHIP-1, as overexpression of dominant-negative SHIP-2 in SHIP-1-deficient primary macrophages resulted in enhanced phagocytic efficiency. Likewise, specific knockdown of SHIP-2 expression using siRNA resulted in enhanced phagocytosis. Finally, analysis of the molecular mechanism of SHIP-2 down-regulation of phagocytosis revealed that SHIP-2 down-regulates upstream activation of Rac. Thus, we conclude that SHIP-2 is a novel negative regulator of FcgammaR-mediated phagocytosis independent of SHIP-1.
Figures
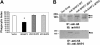


Similar articles
-
Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol polyphosphate phosphatase regulates NF-kappa B-mediated gene transcription by phagocytic Fc gamma Rs in human myeloid cells.J Immunol. 2002 Oct 15;169(8):4370-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.8.4370. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12370370
-
Regulation of FcgammaR-stimulated phagocytosis by the 72-kDa inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase: SHIP1, but not the 72-kDa 5-phosphatase, regulates complement receptor 3 mediated phagocytosis by differential recruitment of these 5-phosphatases to the phagocytic cup.Blood. 2007 Dec 15;110(13):4480-91. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-02-073874. Epub 2007 Aug 6. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17682126
-
The Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol 5-phosphatase negatively regulates Fcgamma receptor-mediated phagocytosis through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-bearing phagocytic receptors.Blood. 2002 Nov 1;100(9):3374-82. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-03-0787. Blood. 2002. PMID: 12384440
-
The role of the inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases in cellular function and human disease.Biochem J. 2009 Apr 1;419(1):29-49. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081673. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19272022 Review.
-
Role of Src homology 2-containing-inositol 5'-phosphatase (SHIP) in mast cells and macrophages.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Feb;31(Pt 1):286-91. doi: 10.1042/bst0310286. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12546703 Review.
Cited by
-
Fcgamma receptor signaling in phagocytes.Int J Hematol. 2006 Oct;84(3):210-6. doi: 10.1532/IJH97.06140. Int J Hematol. 2006. PMID: 17050193 Review.
-
LyGDI, a novel SHIP-interacting protein, is a negative regulator of FcγR-mediated phagocytosis.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021175. Epub 2011 Jun 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21695085 Free PMC article.
-
SHIP-1 increases early oxidative burst and regulates phagosome maturation in macrophages.J Immunol. 2008 Jun 1;180(11):7497-505. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.11.7497. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18490750 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol Kinases and Phosphatases in Entamoeba histolytica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Jun 6;9:150. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00150. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31245297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocytosis and the internalization of pathogenic organisms: focus on phosphoinositides.F1000Res. 2020 May 15;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-368. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.22393.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32494357 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aderem A, Underhill DM. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17: 593-623. - PubMed
-
- Daeron M. Fc receptor biology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15: 203-234. - PubMed
-
- Cooney DS, Phee H, Jacob A, Coggeshall KM. Signal transduction by human-restricted Fc gamma RIIa involves three distinct cytoplasmic kinase families leading to phagocytosis. J Immunol. 2001;167: 844-854. - PubMed
-
- Chacko GW, Duchemin A-M, Coggeshall KM, et al. Clustering of the platelet Fcγ receptor induces noncovalent association with the tyrosine kinase p72syk. J Biol Chem. 1994;269: 32435-32440. - PubMed
-
- Chacko GW, Brandt JT, Coggeshall KM, Anderson CL. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and p72Syk noncovalently associate with the low affinity Fc gamma receptor on human platelets through an ITAM: reconstitution with synthetic phosphopeptides. J Biol Chem. 1996;271: 10775-10781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

