Apoptosis caused by p53-induced protein with death domain (PIDD) depends on the death adapter protein RAIDD
- PMID: 16183742
- PMCID: PMC1242316
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506475102
Apoptosis caused by p53-induced protein with death domain (PIDD) depends on the death adapter protein RAIDD
Abstract
The p53 tumor suppressor promotes cell cycle arrest or apoptosis in response to diverse stress stimuli. p53-mediated cell death depends in large part on transcriptional up-regulation of target genes. One of these targets, P53-induced protein with a death domain (PIDD), was shown to function as a mediator of p53-dependent apoptosis. Here we show that PIDD is a cytoplasmic protein, and that PIDD-induced apoptosis and growth suppression in embryonic fibroblasts depend on the adaptor protein receptor-interacting protein (RIP)-associated ICH-1/CED-3 homologous protein with a death domain (RAIDD). We provide evidence that PIDD-induced cell death is associated with the early activation of caspase-2 and later activation of caspase-3 and -7. Our results also show that caspase-2(-/-), in contrast to RAIDD(-/-), mouse embryonic fibroblasts, are only partially resistant to PIDD. Our findings suggest that caspase-2 contributes to PIDD-mediated cell death, but that it is not the sole effector of this pathway.
Figures
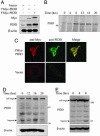
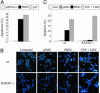
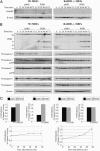
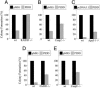
Similar articles
-
DNA damage- and stress-induced apoptosis occurs independently of PIDD.Apoptosis. 2009 Sep;14(9):1039-49. doi: 10.1007/s10495-009-0375-1. Apoptosis. 2009. PMID: 19575295
-
Functional connection between p53 and caspase-2 is essential for apoptosis induced by DNA damage.Oncogene. 2006 Sep 14;25(41):5683-92. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209569. Epub 2006 May 1. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16652156
-
Caspase-2 is required for cell death induced by cytoskeletal disruption.Oncogene. 2008 May 29;27(24):3393-404. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1211005. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18193089
-
Total recall: the role of PIDDosome components in neurodegeneration.Trends Mol Med. 2023 Dec;29(12):996-1013. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.08.008. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Trends Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37716905 Review.
-
PIDD1 in cell cycle control, sterile inflammation and cell death.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Apr 29;50(2):813-824. doi: 10.1042/BST20211186. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 35343572 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of caspase-2 in stress-induced apoptosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2010 Jun;14(6A):1212-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01037.x. Epub 2010 Feb 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20158568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HSP110, caspase-3 and -9 expression in physiological apoptosis and apoptosis induced by in vivo embryonic exposition to all-trans retinoic acid or irradiation during early mouse eye development.J Anat. 2007 May;210(5):532-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00719.x. J Anat. 2007. PMID: 17451530 Free PMC article.
-
NPM1 directs PIDDosome-dependent caspase-2 activation in the nucleolus.J Cell Biol. 2017 Jun 5;216(6):1795-1810. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201608095. Epub 2017 Apr 21. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28432080 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic spectrum associated with a CRADD founder variant underlying frontotemporal predominant pachygyria in the Finnish population.Eur J Hum Genet. 2019 Aug;27(8):1235-1243. doi: 10.1038/s41431-019-0383-8. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Eur J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30914828 Free PMC article.
-
The enigma of caspase-2: the laymen's view.Cell Death Differ. 2009 Feb;16(2):195-207. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2008.170. Epub 2008 Nov 21. Cell Death Differ. 2009. PMID: 19023332 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levine, A. J. (1997) Cell 88, 323-331. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein, B., Lane, D. & Levine, A. J. (2000) Nature 408, 307-310. - PubMed
-
- Vousden, K. H. (2000) Cell 103, 691-694. - PubMed
-
- Soengas, M. S., Alarcon, R. M., Yoshida, H., Giaccia, A. J., Hakem, R., Mak, T. W. & Lowe, S. W. (1999) Science 284, 156-159. - PubMed
-
- Schuler, M., Bossy-Wetzel, E., Goldstein, J. C., Fitzgerald, P. & Green, D. R. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 7337-7342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

