Small RNA genes expressed from Staphylococcus aureus genomic and pathogenicity islands with specific expression among pathogenic strains
- PMID: 16183745
- PMCID: PMC1242290
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0503838102
Small RNA genes expressed from Staphylococcus aureus genomic and pathogenicity islands with specific expression among pathogenic strains
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Nov 15;102(46):16905
Abstract
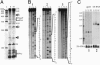
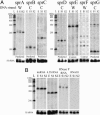
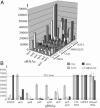
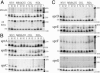
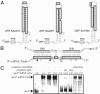
Small RNA (sRNA) genes are expressed in all organisms, primarily as regulators of translation and message stability. We have developed comparative genomic approaches to identify sRNAs that are expressed by Staphylococcus aureus, the most common cause of hospital-acquired infections. This study represents an in-depth analysis of the RNome of a Gram-positive bacterium. A set of sRNAs candidates were identified in silico within intergenic regions, and their expression levels were monitored by using microarrays and confirmed by Northern blot hybridizations. Two sRNAs were also detected directly from purification and RNA sequence determination. In total, at least 12 sRNAs are expressed from the S. aureus genome, five from the core genome and seven from pathogenicity islands that confer virulence and antibiotic resistance. Three sRNAs are present in multiple (two to five) copies. For the sRNAs that are conserved throughout the bacterial phylogeny, their secondary structures were inferred by phylogenetic comparative methods. In vitro binding assays indicate that one sRNA encoded within a pathogenicity island is a trans-encoded antisense RNA regulating the expression of target genes at the posttranscriptional level. Some of these RNAs show large variations of expression among pathogenic strains, suggesting that they are involved in the regulation of staphylococcal virulence.
Figures

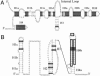
Similar articles
-
Identification of bacterial small non-coding RNAs: experimental approaches.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Jun;10(3):257-61. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2007.05.003. Epub 2007 Jun 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17553733 Review.
-
A Staphylococcus aureus small RNA is required for bacterial virulence and regulates the expression of an immune-evasion molecule.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Jun 3;6(6):e1000927. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000927. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20532214 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus multiresistance plasmid pSK41: analysis of the replication region, initiator protein binding and antisense RNA regulation.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Jan;51(2):497-509. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03843.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 14756789
-
Identification of essential genes in Staphylococcus aureus by construction and screening of conditional mutant library.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;416:297-305. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-321-9_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18392975
-
How to find small non-coding RNAs in bacteria.Biol Chem. 2005 Dec;386(12):1219-38. doi: 10.1515/BC.2005.140. Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16336117 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic and transcriptomic profiling of Staphylococcus aureus surface LPXTG-proteins: correlation with agr genotypes and adherence phenotypes.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Nov;11(11):1123-39. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.014191. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22843989 Free PMC article.
-
Cis-encoded non-coding antisense RNAs in streptococci and other low GC Gram (+) bacterial pathogens.Front Genet. 2015 Mar 26;6:110. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00110. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25859258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The expression of small regulatory RNAs in clinical samples reflects the different life styles of Staphylococcus aureus in colonization vs. infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037294. Epub 2012 May 22. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22629378 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental approaches to identify non-coding RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 25;34(2):635-46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj469. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16436800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative genomics reveals 104 candidate structured RNAs from bacteria, archaea, and their metagenomes.Genome Biol. 2010;11(3):R31. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-3-r31. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Genome Biol. 2010. PMID: 20230605 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

